Mutations causing syndromic autism define an axis of synaptic pathophysiology.
Benjamin D Auerbach, Emily K Osterweil, Mark F Bear
Index: Nature 480 , 63-8, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Tuberous sclerosis complex and fragile X syndrome are genetic diseases characterized by intellectual disability and autism. Because both syndromes are caused by mutations in genes that regulate protein synthesis in neurons, it has been hypothesized that excessive protein synthesis is one core pathophysiological mechanism of intellectual disability and autism. Using electrophysiological and biochemical assays of neuronal protein synthesis in the hippocampus of Tsc2(+/-) and Fmr1(-/y) mice, here we show that synaptic dysfunction caused by these mutations actually falls at opposite ends of a physiological spectrum. Synaptic, biochemical and cognitive defects in these mutants are corrected by treatments that modulate metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in opposite directions, and deficits in the mutants disappear when the mice are bred to carry both mutations. Thus, normal synaptic plasticity and cognition occur within an optimal range of metabotropic glutamate-receptor-mediated protein synthesis, and deviations in either direction can lead to shared behavioural impairments.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
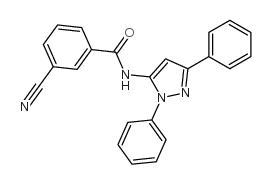 |
CDPPB
CAS:781652-57-1 |
C23H16N4O |
|
Enhancement of extinction learning attenuates ethanol-seekin...
2014-05-28 [J. Neurosci. 34(22) , 7562-74, (2014)] |
|
The mGluR5 positive allosteric modulator, CDPPB, ameliorates...
2015-01-01 [Neurobiol. Dis. 73 , 163-73, (2014)] |
|
Therapeutic effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 pos...
2013-10-01 [Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 27(5) , 483-8, (2013)] |
|
mGlu₅-GABAB interplay in animal models of positive, negative...
2015-09-01 [Neurochem. Int. 88 , 97-109, (2015)] |
|
Dose-dependent effect of CDPPB, the mGluR5 positive alloster...
2009-01-01 [Neuropharmacology 57(5-6) , 531-8, (2009)] |