| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
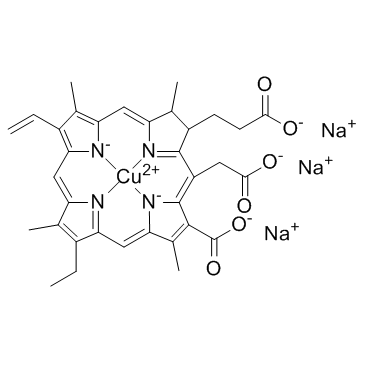 |
Chlorophyllin
CAS:11006-34-1 |
|
![Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/016/191-30-0.png) |
Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene
CAS:191-30-0 |