Telbivudine prevents vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus from women with high viral loads: a prospective long-term study.
Quanxin Wu, Hongfei Huang, Xiaowen Sun, Meimin Pan, Yun He, Shun Tan, Yi Zeng, Li Li, Guohong Deng, Zehui Yan, Dengming He, Junnan Li, Yuming Wang
Index: Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 13 , 1170-6, (2015)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a leading cause of liver diseases. We investigated the efficacy and safety of telbivudine in preventing transmission of HBV from hepatitis B e antigen-positive pregnant women with high viral loads to their infants in an open-label study.We performed a prospective study of 450 hepatitis B e antigen-positive pregnant women with HBV DNA levels greater than 10(6) IU/mL; 279 women received telbivudine (600 mg/d) during weeks 24 to 32 of gestation, and 171 women who were unwilling to take antiviral drugs participated as controls. All newborns were vaccinated with a recombinant HBV vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin, according to a standard immunoprophylaxis procedure. Mother-to-child transmission of HBV was determined by detection of hepatitis B surface antigen and HBV DNA in the infant 6 months after birth.None of the infants whose mothers were given telbivudine tested positive for of hepatitis B surface antigen at 6 months, compared with 14.7% of infants in the control group (P = 5.317 × 10(-8)). Levels of HBV DNA also decreased among women given telbivudine; 40 of 172 (23.2%) women given telbivudine had undetectable HBV DNA levels before delivery, compared with none of the controls. A significantly higher proportion of women given telbivudine had undetectable levels of HBV DNA in cord blood (99.1%) than controls (61.5%; P = 1.195 × 10(-22)). No severe adverse events or complications were observed in women or infants.Telbivudine significantly reduces vertical transmission of HBV from pregnant women to their infants; it is safe and well tolerated by women and infants. Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry Health Care Providers ID: 26592; Government number: Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) 30830090, 30972598; and Third Military Medical University Key Project for Clinical Research: 2012XLC05).Copyright © 2015 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
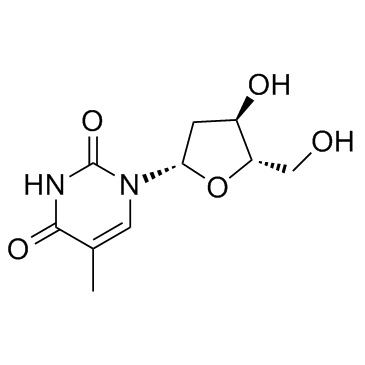 |
Telbivudine
CAS:3424-98-4 |
C10H14N2O5 |
|
Cell Fusion Connects Oncogenesis with Tumor Evolution.
2015-07-01 [Am. J. Pathol. 185 , 2049-60, (2015)] |
|
In vitro activity and resistance profile of samatasvir, a no...
2014-08-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(8) , 4431-42, (2014)] |
|
Telbivudine therapy may shape CD4(+) T-cell response to prev...
2015-03-01 [Liver Int. 35(3) , 834-45, (2015)] |
|
Comparative oncogenomics identifies PSMB4 and SHMT2 as poten...
2014-06-01 [Cancer Res. 74(11) , 3114-26, (2014)] |
|
Cost-effectiveness analysis of antiviral therapies for hepat...
2015-03-01 [Clin. Drug Investig. 35(3) , 197-209, (2015)] |