Electrophysiological and antiarrhythmic effects of the novel antiarrhythmic agent AZD7009: a comparison with azimilide and AVE0118 in the acutely dilated right atrium of the rabbit in vitro.
Lena Löfberg, Ingemar Jacobson, Leif Carlsson
Index: Europace 8(7) , 549-57, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To compare the electrophysiological and antiarrhythmic effects of AZD7009, azimilide, and AVE0118 in the acutely dilated rabbit atria in vitro.In the isolated Langendorf-perfused rabbit heart, the atrial effective refractory period (AERP) and the inducibility of atrial fibrillation (AF) were measured at increasing concentrations of AZD7009 (0.1-3 microM), azimilide (0.1-3 microM), and AVE0118 (0.3-10 microM). In separate groups of atria, termination of sustained AF was assessed. In non-dilated atria, the AERP was 82+/-1.3 ms (mean+/-SEM) and AF could not be induced. Dilation significantly reduced the AERP to 49+/-1.0 ms (P<0.001) and 92% of the atria became inducible. Perfusion with AZD7009, azimilide, and AVE0118 concentration-dependently increased the AERP and reduced the AF inducibility. At the highest concentrations of AZD7009, azimilide, and AVE0118, AERP and AF inducibility changed from 50+/-4.5 to 136+/-6.6 ms and 80 to 0% (both P<0.001) from 51+/-3.0 to 105+/-9.9 ms (P<0.001) and 80 to 0% (P<0.01) and from 46+/-2.8 to 85+/-6.0 ms and 90 to 0% (both P<0.001). Restoration of sinus rhythm was seen in 6/6, 5/6, and 5/6 hearts perfused with AZD7009, azimilide, and AVE0118, respectively.In the dilated rabbit atria, AZD7009, azimilide, and AVE0118 concentration-dependently increased AERP, effectively prevented AF induction, and rapidly restored sinus rhythm.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
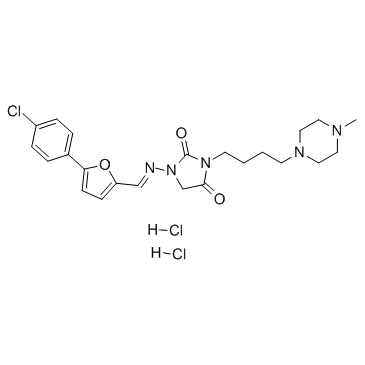 |
Azimilide (Dihydrochloride)
CAS:149888-94-8 |
C23H30Cl3N5O3 |
|
Azimilide dihydrochloride: a new class III anti-arrhythmic a...
2000-11-01 [Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 9(11) , 2705-15, (2000)] |
|
Azimilide for the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial f...
2008-02-01 [J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 19(2) , 172-7, (2008)] |
|
Role of drug therapy for sustained ventricular tachyarrhythm...
2008-08-01 [Cardiol. Clin. 26(3) , 405-18, vi, (2008)] |
|
Effects of azimilide on the muscarinic acetylcholine recepto...
2007-11-01 [J. Pharmacol. Sci. 105(3) , 229-39, (2007)] |
|
Inhibitory effect of azimilide on Na+/Ca2+ exchange current ...
2010-01-01 [J. Pharmacol. Sci. 114(1) , 111-4, (2010)] |