Divalent cations reduce depolarization of primary afferent terminations by GABA.
D R Curtis, B D Gynther
Index: Brain Res. 422(1) , 192-5, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Divalent metal cations, including zinc, cadmium, cobalt, nickel, strontium, manganese, magnesium and calcium, reduced the depolarization by microelectrophoretic gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and piperidine-4-sulphonic acid of the central terminations of muscle group Ia primary afferent fibres in the cat spinal cord without affecting the inhibition by GABA of the firing of spinal interneurones. There thus appears to be a difference in either the interaction of GABA with recognition sites, or in the mechanism by which such interaction activates chloride ionophores, at GABA-mediated bicuculline-sensitive synapses on the central terminals of peripheral primary afferent neurones and those on neurones located within the central nervous system.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
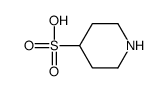 |
4-BROMO-BENZENESULFONIC ACID
CAS:72450-62-5 |
C5H11NO3S |
|
Modulation of [3H]diazepam binding in rat cortical membranes...
1985-04-01 [J. Neurochem. 44(4) , 1162-7, (1985)] |
|
Effects of GABA(A) receptor partial agonists in primary cult...
2001-06-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 133(4) , 539-49, (2001)] |
|
Inhibition of rabbit brain 4-aminobutyrate transaminase by s...
2006-05-14 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 71(10) , 1510-9, (2006)] |
|
Post-tetanic influences on primary afferent depolarization i...
1989-01-01 [Exp. Brain Res. 74(2) , 365-74, (1989)] |
|
On the probable absence of GABA receptors on the termination...
1986-01-01 [Exp. Brain Res. 64(1) , 114-8, (1986)] |