Comparison of the antimuscarinic and antispasmodic actions of racemic oxybutynin and desethyloxybutynin and their enantiomers with those of racemic terodiline.
E R Smith, S E Wright, G Aberg, Y Fang, J R McCullough
Index: Arzneimittelforschung 48(10) , 1012-8, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Racemic oxybutynin (CAS 1508-65-2) is used clinically to treat urinary incontinence and reportedly undergoes N-deethylation to metabolites R- and/or S-desethyloxybutynin. To assess the role of these metabolites in the therapeutic effects of oxybutynin, the antimuscarinic and antispasmodic effects of RS-, R- and S-oxybutynin, RS-, R- and S-desethyloxybutynin and, for comparative purposes, RS-terodiline (CAS 7082-21-5) on isolated strips of guinea pig bladder, were examined. All of these compounds exhibited antimuscarinic activity: they competitively antagonized carbachol-induced contractions, with mean pA2 values (+/- S.E.) of 8.91 +/- 0.20, 8.80 +/- 0.27, 7.09 +/- 0.13, 8.55 +/- 0.32, 9.04 +/- 0.32, 7.31 +/- 0.35 and 6.77 +/- 0.22, respectively. Consistent with an antispasmodic action, all of the compounds produced similar inhibition of potassium-induced contraction; the mean IC50 values for reducing responses to 137.7 mmol/l potassium were between 2.22 and 5.68 mumol/l. Thus, RS- and R-oxybutynin and RS- and R-desethyloxybutynin exhibited high antimuscarinic activity relative to their antispasmodic activity, while S-oxybutynin, S-desethyloxybutynin and RS-terodiline exhibited relatively weak antimuscarinic activity. It is concluded that deethylation of oxybutynin to desethyloxybutynin does not appreciably alter its antimuscarinic or antispasmodic activity and that R- and/or S-desethyloxybutynin probably contribute significantly to the pharmacological properties of oxybutynin in humans. In addition, since the relative potency of the antimuscarinic-to-antispasmodic actions of S-oxybutynin was equivalent to that of RS-terodiline, S-oxybutynin deserves consideration for development as a single-enantiomer drug for the treatment of urinary incontinence. It may produce the same beneficial therapeutic effects as both RS-terodiline and RS-oxybutynin but, like RS-terodiline, produce a lower incidence of antimuscarinic side-effects than seen with RS-oxybutynin.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
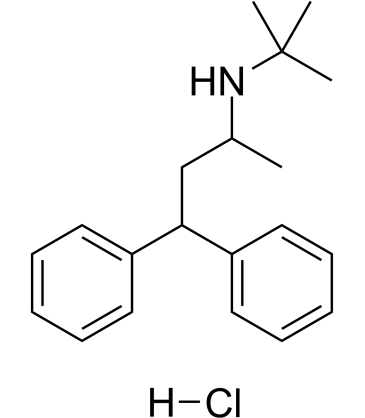 |
Terodiline hydrochloride
CAS:7082-21-5 |
C20H28ClN |
|
Action potentials, contraction, and membrane currents in gui...
1999-09-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290(3) , 1417-26, (1999)] |
|
Comparison of the effects of NS-21 and terodiline on the QTc...
1998-01-01 [Gen. Pharmacol. 30(1) , 137-42, (1998)] |
|
CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes of patients with terodiline car...
2000-07-01 [Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 50(1) , 77-80, (2000)] |
|
Inhibition of cardiac inward-rectifier K+ current by terodil...
1999-07-01 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 370(3) , 319-27, (1999)] |
|
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic assessment of the effects of...
2001-01-01 [Xenobiotica 31(8-9) , 633-50, (2001)] |