Surface area and crystallinity of Form A of chloramphenicol palmitic and stearic esters: which one is the limiting factor in the enzymatic hydrolysis?
F Forni, V Iannuccelli, R Cameroni
Index: J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 39(12) , 1041-3, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Chloramphenicol stearic and palmitic esters in the polymorphic Form A, when ground for 85 h showed an in-vitro enzymatic hydrolysis rate constant (Khydr), the value of which was the same as that of a commercial Form B. The increase in the rate of the enzymatic hydrolysis was not related to the specific surface area as shown by the fact that the micronized Form A, having a higher specific surface area value than ground Form A, showed the same Khydr as the unground Form A. The Khydr value of the ground Form A could be the result of an increase in the crystalline disorder brought about by the grinding process.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
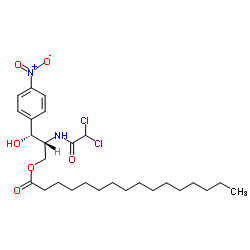 |
Chloramphenicol palmitate
CAS:530-43-8 |
C27H42Cl2N2O6 |
|
Structural, electronic, thermodynamical and charge transfer ...
2013-01-15 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 101 , 335-42, (2013)] |
|
Metabolism of some drugs by intestinal lactobacilli and thei...
1986-01-01 [Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 58(1) , 11-5, (1986)] |
|
The effect of exocrine pancreatic function on chloramphenico...
1988-04-01 [Pediatr. Res. 23(4) , 388-92, (1988)] |
|
Comparative bioavailability of intravenous and oral chloramp...
1984-04-01 [J. Clin. Pharmacol. 24(4) , 181-6, (1984)] |
|
Arthroderma benhamiae infection in a rabbit.
2001-08-01 [J. Vet. Med. Sci. 63(8) , 929-31, (2001)] |