Alterations of protein complexes and pathways in genetic information flow and response to stimulus contribute to Escherichia coli resistance to balofloxacin.
Hui Li, Jian-Yi Pan, Xian-Jie Liu, Jun-Xia Gao, Hong-Kai Wu, Chao Wang, Xuan-Xian Peng
Index: Mol. Biosyst. 8(9) , 2303-11, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Protein-protein interactions are important biological processes and essential for a global understanding of cell functions. To date, little is known about the protein interactions and roles of the protein interacting networks and protein complexes in bacterial resistance to antibiotics. In the present study, we investigated protein complexes in Escherichia coli exposed to an antibiotic balofloxacin (BLFX). One homomeric and eight heteromeric protein complexes involved in BLFX resistance were detected. Potential roles of these complexes that are played in BLFX resistance were characterized and categorized into four functional areas: information streams, monosaccharide metabolism, response to stimulus and amino acid metabolic processes. Protein complexes involved in information streams and response to stimulus played more significant roles in the resistance. These results are consistent with previously published mechanisms on the acquired quinolone-resistance through the GyrA-GyrB complex, and two novel antibiotic-resistant pathways were identified: upregulation of genetic information flow and alteration of the response to a stimulus. The balance of the two pathways will be a viable means of reducing BLFX-resistance.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
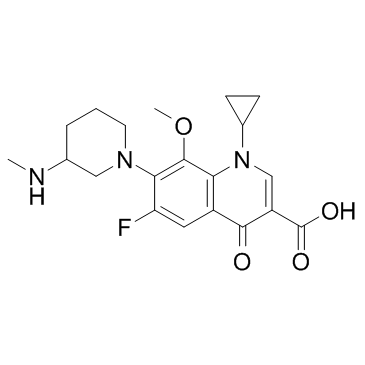 |
Balofloxacin
CAS:127294-70-6 |
C20H24FN3O4 |
|
Determination of the new fluoroquinolone balofloxacin and it...
1995-06-01 [Arzneimittelforschung 45(6) , 716-8, (1995)] |
|
Photoallergenicity of a fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent ...
1998-01-01 [Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 11(4-5) , 232-40, (1998)] |
|
Gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin, and balofloxacin resistance due ...
2009-01-01 [Ophthalmic Res. 42(1) , 43-8, (2009)] |
|
High performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionizati...
2007-05-01 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 850(1-2) , 68-73, (2007)] |
|
In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of Q-35, a nov...
1995-01-01 [Chemotherapy 41(2) , 100-12, (1995)] |