| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
D-Xylulose
CAS:551-84-8 |
|
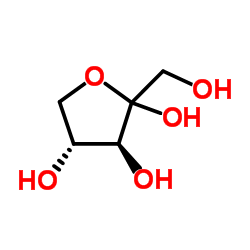 |
L-(+)-Ribulose
CAS:527-50-4 |
|
 |
α-D-Lyxopyranose
CAS:1114-34-7 |