Complexes of amino acids with a crown-ether derivative of 4-styrylpyridine. Monotopic or ditopic?
O A Fedorova, Yu V Fedorov, I E Labazava, E N Gulakova, J Saltiel
Index: Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 10(12) , 1954-62, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
An E-4-styrylpyridine derivative endowed with 18-crown-6 as a substituent (E-1) was prepared and evaluated in acetonitrile as a potential ditopic ligand for protonated amino acids. The interactions of E-1 with the protonated amino acid perchlorates, ClO(4)(-) H(3)N(+)(CH(2))(n)COOH (n = 2, 5 and 10, A2, A5 and A10, respectively), were studied by optical methods, (1)H NMR and mass spectroscopy. Complex formation involves coordination of the ammonium ion at the crown ether moiety of E-1. The spectral changes were evaluated by comparison with results obtained on protonation of E-1 with HClO(4) and on association with ammonium perchlorate. Protonation by the protonated amino acid perchlorates was thwarted due to reversal of carboxyl/pyridinium pK(A) order in acetonitrile relative to water. Evidence for ditopic hydrogen bonding complex formation was especially sought for A10 because its CH(2) chain is sufficiently long to bridge the distance between the crown ether and pyridyl N sites of E-1. Despite some subtle hints to the contrary, the absence of NOE interaction between the pyridyl protons of E-1 and the methylene protons of A10 indicates that the E-1·A10 complex is in the main monotopic, as is the case for A2 and A5. The photophysical and photochemical behaviour of the complexes change significantly on protonation by HClO(4). The optical response of E-1 on binding the amino acids as ammonium salts allows convenient monitoring of complex formation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
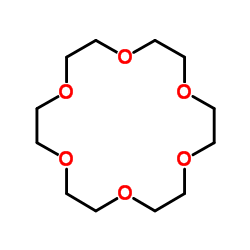 |
18-Crown-6
CAS:17455-13-9 |
C12H24O6 |
|
A novel amino acid analysis method using derivatization of m...
2015-03-21 [Analyst 140(6) , 1965-73, (2015)] |
|
Synthesis and evaluation of candidate PET radioligands for c...
2014-07-01 [Nucl. Med. Biol. 41(6) , 524-35, (2014)] |
|
A novel 2-cyanobenzothiazole-based (18)F prosthetic group fo...
2015-03-28 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 13(12) , 3667-76, (2015)] |
|
Detection of Dinophysistoxin-1 in Clonal Culture of Marine D...
2015-10-01 [Toxins (Basel.) 7 , 3947-59, (2015)] |
|
Quantization of bovine serum albumin by fluorescence enhance...
2012-01-05 [J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 106 , 113-9, (2012)] |