Peptide mimics as substrates for the intestinal peptide transporter.
C S Temple, A K Stewart, D Meredith, N A Lister, K M Morgan, I D Collier, R D Vaughan-Jones, C A Boyd, P D Bailey, J R Bronk
Index: J. Biol. Chem. 273(1) , 20-2, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
4-Aminophenylacetic acid (4-APAA), a peptide mimic lacking a peptide bond, has been shown to interact with a proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter using a number of different experimental approaches. In addition to inhibiting transport of labeled peptides, these studies show that 4-APAA is itself translocated. 4-APAA transport across the rat intact intestine was stimulated 18-fold by luminal acidification (to pH 6.8) as determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); in enterocytes isolated from mouse small intestine the intracellular pH was reduced on application of 4-APAA, as shown fluorimetrically with the pH indicator carboxy-SNARF; 4-APAA trans-stimulated radiolabeled peptide transport in brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat renal cortex; and in Xenopus oocytes expressing PepT1, 4-APAA produced trans-stimulation of radiolabeled peptide efflux, and as determined by HPLC, was a substrate for translocation by this transporter. These results with 4-APAA show for the first time that the presence of a peptide bond is not a requirement for rapid translocation through the proton-linked oligopeptide transporter (PepT1). Further investigation will be needed to determine the minimal structural requirements for a molecule to be a substrate for this transporter.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
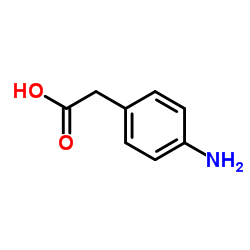 |
(4-Aminophenyl)acetic acid
CAS:1197-55-3 |
C8H9NO2 |
|
4-aminomethylbenzoic acid is a non-translocated competitive ...
1998-11-01 [J. Physiol. 512 ( Pt 3) , 629-34, (1998)] |
|
Preparation of 4-aminophenylacetic acid derivatives with pro...
2006-09-01 [Acta. Pharm. 56(3) , 273-84, (2006)] |
|
p-Aminophenylacetic acid-mediated synthesis of monodispersed...
2009-10-15 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 338(2) , 468-73, (2009)] |
|
Inhibition of Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced colitis ...
2005-03-01 [Dig. Dis. Sci. 50(3) , 565-73, (2005)] |