Adenosine and ATP effects on isolated guinea pig gallbladder.
P Naughton, H P Baer, A S Clanachan, G W Scott
Index: Pflugers Arch. 399(1) , 42-5, (1983)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Effects of adenosine, ATP and several derivatives of adenosine were measured in isolated strips of guinea pig gallbladder. Adenosine caused relaxations which were antagonized by theophylline and potentiated by an inhibitor of adenosine uptake, 6-(1-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzylthio)-guanosine (HNBTG). Among several adenosine derivatives, 2-chloroadenosine and 5'-N-ethylcarboxy-midoadenosine were similarly effective while 1-N6-phenylisopropyladenosine was only a weak relaxant. None of the derivatives caused maximal relaxations at 100 microM, and thus absolute potencies could not be determined. ATP caused predominantly contractile effects, with relaxations sometimes being evident at high concentrations. Indomethacin abolished contractile effects of ATP, suggesting prostaglandin involvement, and only relaxations were evident in its presence. Adenosine deaminase abolished the effects of adenosine and partly reduced the relaxant effects of ATP in the presence of indomethacin. In view of the low potency of adenosine and ATP, physiological roles for these compounds in gallbladder motility are not readily evident.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
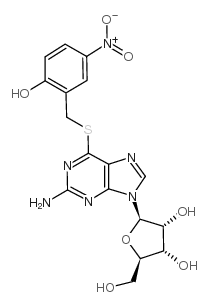 |
s-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzyl)-6-thioguanosine
CAS:41094-07-9 |
C17H18N6O7S |
|
Inhibitors of nucleoside transport. A structure-activity stu...
1975-10-01 [J. Med. Chem. 18 , 968, (1975)] |
|
Neurotensin stimulates Cl(-) secretion in human colonic muco...
2000-08-01 [Gastroenterology 119(2) , 348-57, (2000)] |
|
Mechanism of urate production by guinea-pig ileum.
1986-01-01 [Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 195 Pt B , 239-43, (1986)] |
|
Potentiation of methotrexate lymphocytotoxicity in vitro by ...
1989-03-01 [Br. J. Cancer 59(3) , 381-4, (1989)] |
|
The effect of pH on interaction of nitrobenzylthioinosine an...
1985-07-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 27(6) , 662-5, (1985)] |