| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
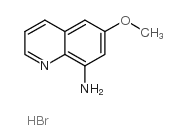 |
Poly(ethylene glycol) bis(2-ethylhexanoate)
CAS:312693-53-1 |
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Poly(ethylene glycol) bis(2-ethylhexanoate)
CAS:312693-53-1 |