PTH stimulated growth and decreased Col-X deposition are phosphotidylinositol-3,4,5 triphosphate kinase and mitogen activating protein kinase dependent in avian sterna.
X Wang, L H Dong, J T Li, X L Li, X L Ma, Y F Zheng
Index: Anat. Rec. (Hoboken.) 293(2) , 225-34, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Type X collagen (Col-X) deposition is a marker of terminal differentiation during chondrogenesis, in addition to appositional growth and apoptosis. The parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone related peptide (PTH/PTHrP) receptor, or PPR, is a G-Protein coupled receptor (GPCR), which activates several downstream pathways, moderating chondrocyte differentiation, including suppression of Col-X deposition. An Avian sterna model was used to analyze the PPR GPCR downstream kinase role in growth rate and extracellular matrix (ECM) including Col-II, IX, and X. Phosphatidylinositol kinase (PI3K), mitogen activating protein kinase (MAPK) and protein kinase A (PKA) were inhibited with specific established inhibitors LY294002, PD98059, and H89, respectively to test the hypothesis that they could reverse/inhibit the PTH/PTHrP pathway. Excised E14 chick sterna were PTH treated with or without an inhibitor and compared to controls. Sternal length was measured every 24 hr. Cultured sterna were immuno-stained using specific antibodies for Col-II, IX, or X and examined via confocal microscopy. Increased growth in PTH-treated sterna was MAPK, PI3K, and PKA dose dependent, suggesting growth was regulated through multiple pathways. Col-X deposition was rescued in PTH-treated sterna in the presence of PI3K or MAPK inhibitors, but not with the PKA inhibitor. All three inhibitors moderately disrupted Col-II and Col-IX deposition. These results suggest that PTH can activate multiple pathways during chondrocyte differentiation.2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
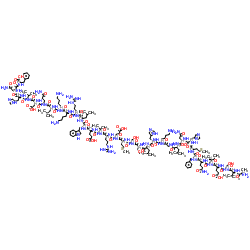 |
pTH (1-34) (bovine)
CAS:12583-68-5 |
C183H288N54O50S2 |
|
Thyroid hormones enhance the biomechanical functionality of ...
2015-01-01 [Arthritis. Res. Ther. 17 , 28, (2015)] |
|
Identification of a novel parathyroid hormone-responsive gen...
1999-04-01 [Bone 24(4) , 305-13, (1999)] |
|
Functional properties of a synthetic chicken parathyroid hor...
1994-07-01 [J. Bone Miner Res. 9(7) , 1041-6, (1994)] |
|
Comparison of the effects of various lengths of synthetic hu...
1993-01-01 [Bone 14(5) , 717-20, (1993)] |
|
Anomalous effects of hormone fragments on the measurement of...
1996-03-01 [Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 18(2) , 87-99, (1996)] |