Activation of cellulose membranes with 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole or 1-cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate as a basis for the development of immunosensors.
Daniela Stöllner, Frieder W Scheller, Axel Warsinke
Index: Anal. Biochem. 304(2) , 157-65, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Methods for the activation of a cellulose dialysis membrane for immunosensor applications have been developed. For activation two reagents, 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) and 1-cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate (CDAP), were compared with respect to the coupling efficiency for glucose oxidase (GOx) and 1,8-diamino-2,6-dioxaoctane. The maximum level of activation was 2.4 micromol cm(-2) for CDI and 0.2 micromol cm(-2) for CDAP activation. We observed 1.5 microg cm(-2) and 0.4 x 10(-4) U cm(-2) GOx with CDI-activated membranes whereas 1.7 microg cm(-2) and 7.2 x 10(-4) U cm(-2) GOx were observed with CDAP-activated membranes. With 1,8-diamino-2,6-dioxaoctane amino group densities of 0.165 and 0.09 micromol cm(-2) were observed via CDI and CDAP activation, respectively. An amino-modified membrane was used for coupling a ligand (pentapeptide) and an immunoenzymometric assay for hemoglobin A1c was carried out.(c) 2002 Elsevier Science (USA)
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
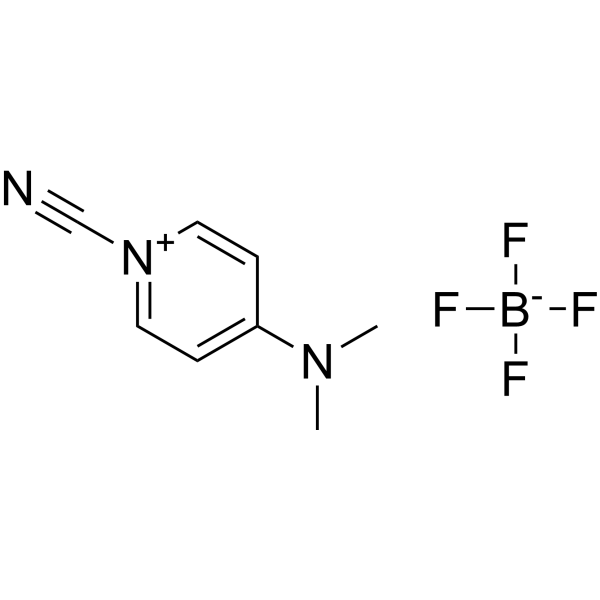 |
CDAP
CAS:59016-56-7 |
C8H10BF4N3 |
|
Preparation and testing of a Haemophilus influenzae Type b/H...
2015-03-24 [Vaccine 33(13) , 1614-9, (2015)] |
|
Preparation and characterization of group A meningococcal ca...
2003-09-01 [Infect. Immun. 71(9) , 5115-20, (2003)] |
|
Surfactant-assisted lipopolysaccharide conjugation employing...
2009-05-15 [Anal. Chem. 81 , 3824-9, (2009)] |
|
Two efficient methods for the conjugation of smooth-form lip...
2011-01-01 [Methods Mol. Biol. 739 , 161-167, (2011)] |
|
Determination of the disulfide structure of sillucin, a high...
2001-04-17 [Biochemistry 40(15) , 4531-8, (2001)] |