Discovery of a quorum-sensing inhibitor of drug-resistant staphylococcal infections by structure-based virtual screening.
Madanahally D Kiran, Nallini Vijayarangan Adikesavan, Oscar Cirioni, Andrea Giacometti, Carmela Silvestri, Giorgio Scalise, Roberto Ghiselli, Vittorio Saba, Fiorenza Orlando, Menachem Shoham, Naomi Balaban
Index: Mol. Pharmacol. 73(5) , 1578-86, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Staphylococci are a major health threat because of increasing resistance to antibiotics. An alternative to antibiotic treatment is preventing virulence by inhibition of bacterial cell-to-cell communication using the quorum-sensing inhibitor RNAIII-inhibiting peptide (RIP). In this work, we identified 2',5-di-O-galloyl-d-hamamelose (hamamelitannin) as a nonpeptide analog of RIP by virtual screening of a RIP-based pharmacophore against a database of commercially available small-molecule compounds. Hamamelitannin is a natural product found in the bark of Hamamelis virginiana (witch hazel), and it has no effect on staphylococcal growth in vitro; but like RIP, it does inhibit the quorum-sensing regulator RNAIII. In a rat graft model, hamamelitannin prevented device-associated infections in vivo, including infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis strains. These findings suggest that hamamelitannin may be used as a suppressor to staphylococcal infections.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
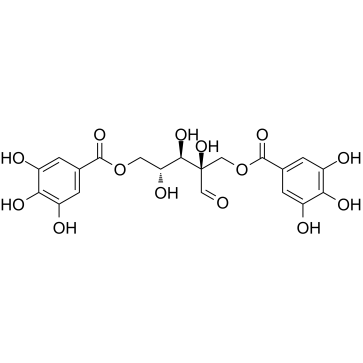 |
Hamamelitannin
CAS:469-32-9 |
C20H20O14 |
|
Quorum sensing inhibitors increase the susceptibility of bac...
2011-06-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55 , 2655-2661, (2011)] |
|
Hamamelitannin from witch hazel (Hamamelis virginiana) displ...
2012-01-27 [J. Nat. Prod. 75 , 26-33, (2012)] |
|
Cerium, chitosan and hamamelitannin as novel biofilm inhibit...
2012-05-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 67 , 1159-62, (2012)] |
|
Genotoxic and antigenotoxic effects of catechin and tannins ...
2003-05-01 [Phytochemistry 63(2) , 199-207, (2003)] |
|
In vivo antibiofilm effect of cerium, chitosan and hamamelit...
2013-01-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 68(1) , 126-30, (2013)] |