A single binding site for dilysine retrieval motifs and p23 within the gamma subunit of coatomer.
C Harter, F T Wieland
Index: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95(20) , 11649-54, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Coatomer, the major component of the coat of COPI transport vesicles, binds both to the dilysine motif of resident membrane proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum and to the cytoplasmic domain of p23, a major type I membrane protein of COPI vesicles. Using a photocrosslinking approach, we find that under native conditions a peptide analogous to the cytoplasmic domain of p23 interacts with coatomer exclusively through its gamma subunit and shares its binding site with a KKXX retrieval motif. However, upon dissociation of coatomer, interaction with various subunits, including an alpha-, beta'-, epsilon-COP subcomplex, of the photoreactive peptide is observed. We suggest that, under physiological conditions, interaction of coatomer with both endoplasmic reticulum retrieval motifs and the cytoplasmic domain of p23 is mediated by gamma-COP.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
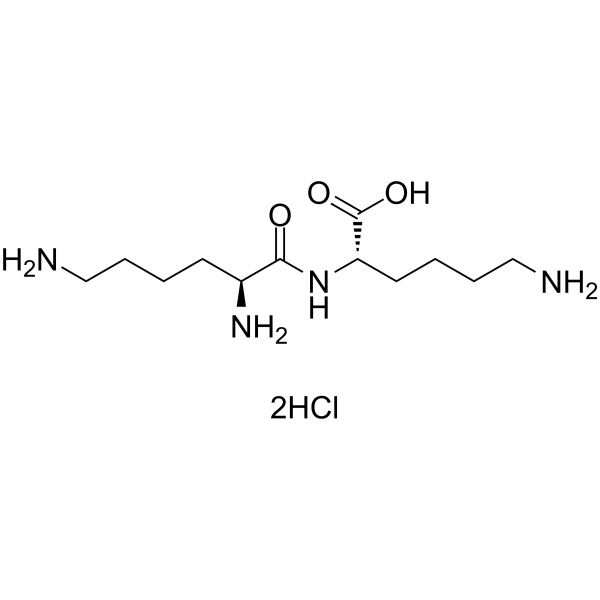 |
h-lys-lys-oh 2hcl
CAS:52123-30-5 |
C12H28Cl2N4O3 |
|
Canine zona pellucida glycoprotein-3: up-scaled production, ...
2015-01-01 [Vaccine 33(1) , 133-40, (2014)] |
|
Intracellular targeting signals contribute to localization o...
2004-06-01 [J. Virol. 78(11) , 5913-22, (2004)] |
|
Targeted gap junction protein constructs reveal connexin-spe...
2002-06-07 [J. Biol. Chem. 277(23) , 20911-8, (2002)] |
|
Peptide binding in OppA, the crystal structures of the perip...
1997-08-12 [Biochemistry 36(32) , 9747-58, (1997)] |
|
Endoplasmic reticulum retention of the large splice variant ...
2005-10-01 [Glycobiology 15(10) , 905-11, (2005)] |