A spectrophotometric method for determination of sphingomyelinase.
S Gatt, T Dinur, Y Barenholz
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 530 , 503, (1978)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A colored derivative of sphingomyelin was synthesized and used as substrate for several sphingomyelinases. The compound is N-omega-trinitrophenyl-aminolaurylsphingosylphosphorylcholine. The rate of hydrolysis of this substrate was compared to that of bovine brain sphingomyelin, labelled with tritium in the choline moiety. The following enzyme preparations were used: homogenate-less debris of brain, assayed at pH 5.0 or 7.4; a solubilized preparation derived from rat brain lysosomes, assayed at pH 5.0 and a purified enzyme of Staphylococcus aureus. With all preparations, the rates of hydrolysis of the yellow derivative were very similar to those of the brain sphingomyelin. Extracts of skin fibroblasts of normal and Niemann-Pick patients as well as amniotic cells were also used. Again, the rates of hydrolysis of the yellow derivative practically equalled those using brain sphingomyelin.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
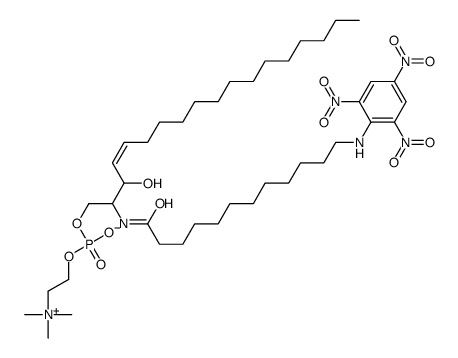 |
TNPAL-Sphingomyelin
CAS:117985-56-5 |
C41H73N6O12P |
|
Rapid phase change of lipid microdomains in giant vesicles i...
2006-02-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1758(2) , 145-53, (2006)] |
|
Interaction between sphingomyelin and oxysterols contributes...
2013-01-01 [Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 3(1) , 17-26, (2013)] |
|
Sphingomyelin metabolism at the plasma membrane: Implication...
2010-01-01 [FEBS Lett. 584(9) , 1887-94, (2010)] |
|
Identification of the teichoic acid phosphorylcholine estera...
2001-03-01 [Mol. Microbiol. 39(6) , 1610-22, (2001)] |
|
Effect of endurance training on the sphingomyelin-signalling...
2004-06-01 [J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 55(2) , 305-13, (2004)] |