| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
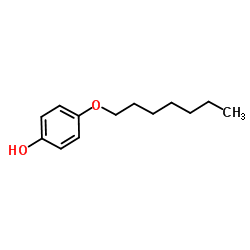 |
4-(Heptyloxy)phenol
CAS:13037-86-0 |
J Mlynarczuk, M H Wrobel, J Kotwica
Index: Theriogenology 81(7) , 877-86, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
The orphan receptor steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1) is involved in the regulation of ovarian steroidogenesis in cows. It is hypothesized that estrogen-like chlorinated compounds might affect SF-1, and thus impair the function of the ovary. Bovine luteal cells from the estrous cycle (Days: 1-5, 6-10, 11-15, and 16-19) were treated for 50 hours with DDT, 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethene, 3,3'4,4'-tetrachlorobiphenyl or 2'2'4,4',5,5'-hexachlorobiphenyl (each at a dose of 10 ng/mL). Luteal cells were also treated with 4-(heptyloxy)phenol (1 × 10(-7) M), an SF-1 agonist, and F0160 (1 × 10(-6) M), an SF-1 blocker, jointly or separately. The secretion of progesterone and oxytocin and the expression of oxytocin precursor (NP-I/OT) messenger RNA were increased (P < 0.05) by all studied xenobiotics and 4-(heptyloxy)phenol, although they were inhibited (P < 0.05) by F0160. However, the xenobiotics did not affect (P > 0.05) SF-1 messenger RNA expression. In summary, SF-1 is involved in the adverse effect of chlorinated xenobiotics on the regulation of the bovine CL. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
4-(Heptyloxy)phenol
CAS:13037-86-0 |
C13H20O2 |
|
Impact of induced fit on ligand binding to the androgen rece...
2005-09-08 [J. Med. Chem. 48 , 5666-74, (2005)] |
|
The expression of Steroidogenic Factor-1 and its role in bov...
2013-04-01 [Anim. Reprod. Sci. , doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2013.01.008, (2013)] |
|
Small molecule agonists of the orphan nuclear receptors ster...
2011-04-14 [J. Med. Chem. 54 , 2266-81, (2011)] |
Home | MSDS/SDS Database Search | Journals | Product Classification | Biologically Active Compounds | Selling Leads | About Us | Disclaimer
Copyright © 2024 ChemSrc All Rights Reserved