| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
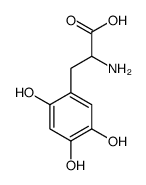 |
6-Hydroxy-DL-DOPA
CAS:21373-30-8 |
|
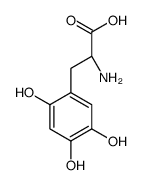 |
6-Hydroxy-L-DOPA
CAS:27244-64-0 |