Eucalyptol is an attractant of the Redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus.
Emily H Kuhns, Xavier Martini, Yolani Tribuiani, Monique Coy, Christopher Gibbard, Jorge Peña, Jiri Hulcr, Lukasz L Stelinski
Index: J. Chem. Ecol. 40(4) , 355-62, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus, is an invasive wood-boring beetle that has become established in the southeastern United States. The beetle transmits the causal pathogen of lethal laurel wilt to susceptible host trees, which include redbay, an important forest community species, and avocado, a valuable food crop. By examining odors of redbay wood, we developed an artificial lure that captured X. glabratus in redbay forests. Eucalyptol was a critical component of the blend for beetle attraction, and eucalyptol alone in large quantities attracted X. glabratus. Furthermore, eucalyptol stimulated boring by X. glabratus into paper arenas. The results suggest that eucalyptol contributes to host selection behavior of X. glabratus and may be useful for management of this pathogen vector.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
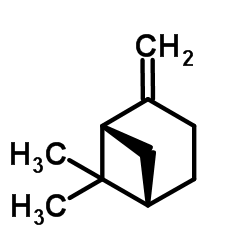 |
Beta-pinene
CAS:18172-67-3 |
C10H16 |
|
Antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity on tumour cells of the...
2015-01-01 [Nat. Prod. Res. , 1-9, (2015)] |
|
Evidence for the existence of organosulfates from beta-pinen...
2007-10-01 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 41(19) , 6678-83, (2007)] |
|
Chemical composition, antimicrobial, insecticidal, phytotoxi...
2014-12-01 [Chin. J. Nat. Med. 12(12) , 901-10, (2014)] |
|
[Aldrichimica Acta 13 , 13, (1980)] |
|
[Tetrahedron Lett. 30 , 6653, (1989)] |