Effect of the cytostatic butyric acid pro-drug, pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate, on the tumorigenicity of cancer cells.
A Aviram, A Rephaeli, M Shaklai, A Nudelman, I Ben-Dror, L Maron, E Rabizadeh
Index: J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 123(5) , 267-71, (1997)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Previously we have shown that pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate (AN-9), a pro-drug of butyric acid (BA), is a differentiation-inducing agent in a variety of cells. In this report, we demonstrate that AN-9 is a cytostatic but not cytotoxic agent in a myelomonocytic cell line (WEHI); thus, the cells were growth-arrested and differentiated. These late changes in the cells were preceded by changes in the expression of the early regulatory genes, c-myc and c-jun. Although initiation of all these events had already occurred after 1 h exposure to AN-9, the tumorigenicity of these cells tested in Balb/c mice was not affected. A marked reduction in the tumorigenicity of AN-9-treated cells was observed after 4 h of exposure. Exposure of the highly metastatic subclone of Lewis lung carcinoma (3LLD122) to AN-9 resulted in a very pronounced effect on the tumorigenicity of these cells tested in C57BL mice. Unlike WEHI cells, the tumorigenicity of 3LLD122 was almost completely diminished after 1 h of exposure. In both cell types a 10-fold higher concentration of BA did not affect the tumorigenicity of the cells as did AN-9.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
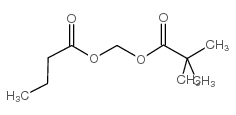 |
AN-9
CAS:122110-53-6 |
C10H18O4 |
|
A phase I study of pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate, a prodrug of ...
2002-07-01 [Clin. Cancer Res. 8(7) , 2142-8, (2002)] |
|
Anticancer derivative of butyric acid (Pivalyloxymethyl buty...
2000-07-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 58(1) , 27-36, (2000)] |
|
Mitoxantrone mediates demethylation and reexpression of cycl...
2003-01-01 [Cancer Biol. Ther. 2(3) , 259-63, (2003)] |
|
Uptake of pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate into leukemic cells and...
2000-12-01 [J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 126(12) , 693-8, (2000)] |
|
An anti-cancer derivative of butyric acid (pivalyloxmethyl b...
1997-01-01 [Br. J. Cancer 75(6) , 850-4, (1997)] |