Biodegradation of phytane (2,6,10,14-tetramethylhexadecane) and accumulation of related isoprenoid wax esters by Mycobacterium ratisbonense strain SD4 under nitrogen-starved conditions.
Roxana A Silva, Vincent Grossi, Héctor M Alvarez
Index: FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 272(2) , 220-8, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The accumulation of storage lipids during the biodegradation of 2,6,10,14-tetramethylhexadecane (phytane) by Mycobacterium ratisbonense strain SD4 grown under nitrogen-starved conditions was investigated. Detailed chemical analysis of intracellular metabolites revealed the existence of (at least) three different pathways for the catabolism of phytane, and the accumulation of significant proportions (39% of the total lipids) of several isoprenoid wax esters formed by condensation of oxidation products of the hydrocarbon. In contrast, triacylglycerols but no wax esters were accumulated by strain SD4 grown on hexadecane, the unbranched homologue of phytane.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
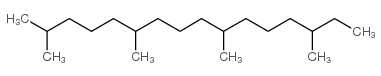 |
phytane
CAS:638-36-8 |
C20H42 |
|
Chemical constituents of Heteroplexis micocephala.
2009-06-01 [J. Nat. Prod. 72 , 1184-90, (2009)] |
|
Production of pristane and phytane in the marine environment...
2011-11-01 [Res. Microbiol. 162(9) , 923-33, (2011)] |
|
Determination of anthropogenic and biogenic compounds on atm...
2010-01-01 [Sci. Total Environ. 408(23) , 5836-44, (2010)] |
|
Cluster of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) associated wit...
2007-01-01 [Environ. Health 6 , 8, (2007)] |
|
Isotopic biogeochemistry of the Oxford Clay Formation (Juras...
1994-01-01 [J. Geol. Soc. London. 151 , 139-52, (1994)] |