Frequency-dependent Escherichia coli chemotaxis behavior.
Xuejun Zhu, Guangwei Si, Nianpei Deng, Qi Ouyang, Tailin Wu, Zhuoran He, Lili Jiang, Chunxiong Luo, Yuhai Tu
Index: Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(12) , 128101, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We study Escherichia coli chemotaxis behavior in environments with spatially and temporally varying attractant sources by developing a unique microfluidic system. Our measurements reveal a frequency-dependent chemotaxis behavior. At low frequency, the E. coli population oscillates in synchrony with the attractant. In contrast, in fast-changing environments, the population response becomes smaller and out of phase with the attractant waveform. These observations are inconsistent with the well-known Keller-Segel chemotaxis equation. A new continuum model is proposed to describe the population level behavior of E. coli chemotaxis based on the underlying pathway dynamics. With the inclusion of a finite adaptation time and an attractant consumption rate, our model successfully explains the microfluidic experiments at different stimulus frequencies.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
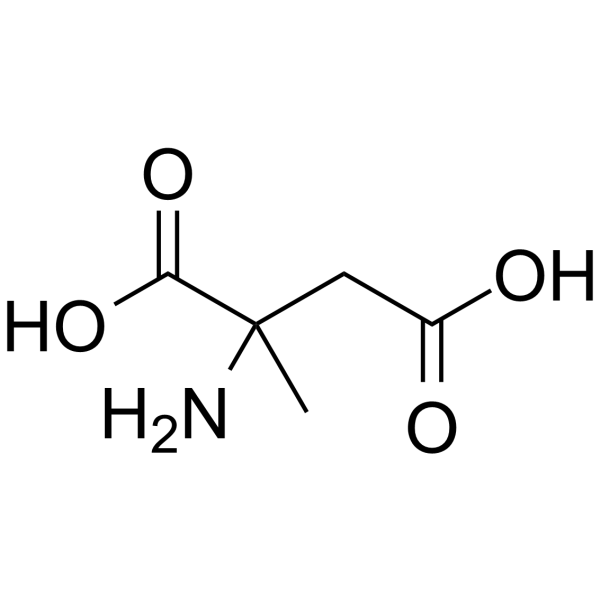 |
2-amino-2-methylsuccinic acid
CAS:2792-66-7 |
C5H9NO4 |
|
Binding of C5-dicarboxylic substrate to aspartate aminotrans...
2005-06-14 [Biochemistry 44(23) , 8218-29, (2005)] |
|
Endothelial nitric oxide production is tightly coupled to th...
2007-01-01 [Nitric Oxide 17 , 115-121, (2007)] |
|
Crystal structures of Escherichia coli aspartate aminotransf...
1994-06-03 [J. Mol. Biol. 239(2) , 285-305, (1994)] |
|
Receptor sensitivity in bacterial chemotaxis.
2002-01-08 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99(1) , 123-7, (2002)] |
|
Role of the L-citrulline/L-arginine cycle in iNANC nerve-med...
2006-09-28 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 546(1-3) , 171-6, (2006)] |