Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad.
J Hartmann, W Reineke, H J Knackmuss
Index: Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 37(39) , 421-428., (1979)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Pseudomonas sp. WR912 was isolated by continuous enrichment in three steps with 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and finally 3,5-dichlorobenzoate as sole source of carbon and energy. The doubling times of the pure culture with these growth substrates were 2.6, 3.3, and 5.2 h, respectively. Stoichiometric amounts of chloride were eliminated during growth. Oxygen uptake rates with chlorinated benzoates revealed low stereospecificity of the initial benzoate 1,2-dioxygenation. Dihydrodi-hydroxybenzoate dehydrogenase, catechol 1,2-dixoygenase, and muconate cycloisomerase activities were found in cell-free extracts. The ortho cleavage activity for catechols appeared to involve induction of isoenzymes with different stereospecificity towards chlorocatechols. A catabolic pathway for chlorocatechols was proposed on the basis of similarity to chlorophenoxyacetate catabolism, and cometabolism of 3,5-dimethylbenzoate by chlorobenzoate-induced cells yielded 2,5-dihydro-2,4-dimethyl-5-oxo-furan-2-acetic acid.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
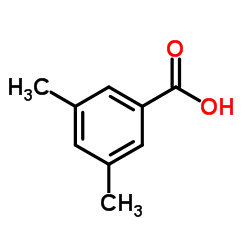 |
3,5-Dimethylbenzoic acid
CAS:499-06-9 |
C9H10O2 |
|
Organotin(IV) based anti-HCV drugs: synthesis, characterizat...
2015-06-14 [Dalton Trans. 44 , 10467-78, (2015)] |
|
Urinary excretion of dimethylhippuric acids in humans after ...
1997-01-01 [Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 69(6) , 491-7, (1997)] |
|
Biological monitoring of experimental human exposure to trim...
1997-06-20 [Sci. Total Environ. 199(1-2) , 73-81, (1997)] |
|
Kinetics of elimination of mesitylene and 3,5-dimethylbenzoi...
1995-05-01 [Toxicol. Lett. 77(1-3) , 259-64, (1995)] |
|
Biosynthesis of a Cyclic Tautomer1of (3-Methylmaleyl)acetone...
1997-09-08 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 238(1) , 197-201, (1997)] |