| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
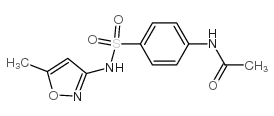 |
N4-Acetylsulfamethoxazole
CAS:21312-10-7 |
T B Vree, M L Vree, J F Nouws
Index: Vet. Q. 9(4) , 378-81, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
The snail Cepaea hortensis is able to acetylate and hydroxylate sulphamethoxazole in a similar way to man. About one percent deacetylation, but no hydroxylation of N4-acetysulphamethoxazole takes place. The relative rates of the metabolic pathways for hydroxylation and acetylation of sulphamethoxazole are equal.
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
N4-Acetylsulfamethoxazole
CAS:21312-10-7 |
C12H13N3O4S |
|
Excretion rates of sulfamethoxazole and N4-acetyl-sulfametho...
1984-07-01 [Vet. Q. 6(3) , 169-73, (1984)] |
|
Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of 12 milligrams of trimethop...
1993-03-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37(3) , 448-52, (1993)] |
|
Sampling the lipogenic hepatic acetyl-CoA pool in vivo in th...
1991-06-15 [J. Biol. Chem. 266(17) , 10912-9, (1991)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics of the trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole combi...
1985-12-01 [Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 20(6) , 575-81, (1985)] |
|
Rapid simultaneous determination of trimethoprim, sulphameth...
1991-01-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 9(6) , 507-10, (1991)] |
Home | MSDS/SDS Database Search | Journals | Product Classification | Biologically Active Compounds | Selling Leads | About Us | Disclaimer
Copyright © 2024 ChemSrc All Rights Reserved