Tetrahydrocurcumin confers protection against amyloid β-induced toxicity.
Shilpa Mishra, Mamata Mishra, Pankaj Seth, Shiv Kumar Sharma
Index: Neuroreport 22(1) , 23-7, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are the hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease. Amyloid β, a primary component of the amyloid plaques, is neurotoxic. Considerable attention has been directed toward identifying compounds with neuroprotective properties. Using rat primary hippocampal cultures, we show that tetrahydrocurcumin (THC), a metabolite of curcumin, shows a protective effect against oligomeric amyloid-β-induced toxicity. We further show that THC reduces amyloid-β-induced (i) increase in the level of reactive oxygen species, (ii) decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential, and (iii) caspase activation. In addition, we show that THC protects human neurons from oligomeric amyloid-β-induced toxicity as well. Thus, THC confers protection against amyloid-β-induced toxicity, and the antioxidant activity may contribute to its protective effect.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
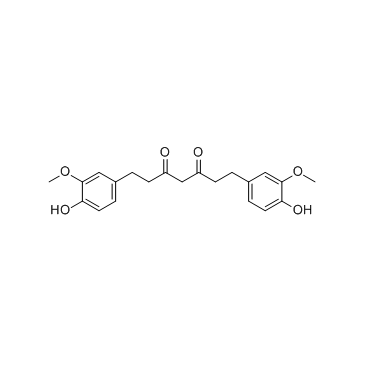 |
Tetrahydrocurcumin
CAS:36062-04-1 |
C21H24O6 |
|
Structure-activity relationship analysis of curcumin analogu...
2013-11-01 [FEBS J. 280(22) , 5829-40, (2013)] |
|
Differential cellular uptake and metabolism of curcuminoids ...
2014-07-14 [Br. J. Nutr. 112(1) , 8-14, (2014)] |
|
Synthesis of quinoline derivatives of tetrahydrocurcumin and...
2013-01-15 [Food Chem. 136(2) , 650-8, (2013)] |
|
Antioxidant combinations protect oral fibroblasts against me...
2013-03-01 [Arch. Oral Biol. 58(3) , 299-310, (2013)] |
|
Inhibition of Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) channel (CRAC)...
2012-11-09 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 428(1) , 56-61, (2012)] |