TGF-β Blood Levels Distinguish Between Influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 Virus Sepsis and Sepsis due to Other Forms of Community-Acquired Pneumonia.
Erick J Rendón-Ramirez, Alejandro Ortiz-Stern, Corazon Martinez-Mejia, Mario C Salinas-Carmona, Adrian Rendon, Viviana L Mata-Tijerina, Adrian G Rosas-Taraco
Index: Viral Immunol. 28 , 248-54, (2015)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
There is a strong interest in finding adequate biomarkers to aid in the diagnosis and prognosis of influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 virus infection. In this study, serum levels of inflammatory cytokines and laboratory markers were evaluated to assess their usefulness as biomarkers of influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 and their association with fatal cases. Serum samples of consecutive patients with a clinical presentation suggestive of influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 and progression to sepsis were evaluated. Serum inflammatory cytokines and routine laboratory tests were performed and correlated with positivity for influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 influenza by real time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and the results of three clinical severity scores (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment [SOFA], CURB-65, and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II [APACHE II]). High SOFA scores and some of its individual components, but not CURB-65 or APACHE II scores, correlate with fatal cases regardless of etiology. Total and unconjugated bilirubin, Ca(++), Cl(-), prothrombin times, and partial thromboplastin times discriminate influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 from other causes of community-acquired pneumonia. High levels of IL-8, IL-10, and IL-17 were increased in influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 patients when compared with controls (p<0.05). IL-6 levels were significantly elevated in influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 patients and non-(H1N1)pdm09 patients when compared with controls (p<0.05). TGF-β serum levels discern between healthy controls, influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 patients, and patients with other causes of community-acquired pneumonia. TGF-β levels were negatively correlated with SOFA on admission in influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 patients. TGF-β levels are a useful tool for differentiating influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 from other causes of pneumonia progressing to sepsis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
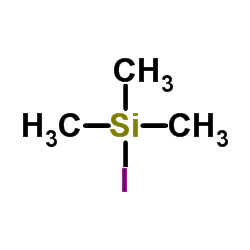 |
Trimethylsilyl iodide
CAS:16029-98-4 |
C3H9ISi |
|
Occurrence, removal, and fate of progestogens, androgens, es...
2014-11-01 [Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 21(22) , 12898-908, (2014)] |
|
Validation of an enzyme immunoassay for the measurement of f...
2014-09-15 [Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 206 , 166-77, (2014)] |
|
[Determination of anabolic steroid hormones in animal muscle...
2006-01-01 [Se Pu 24(1) , 19-22, (2006)] |
|
[Tetrahedron Lett. 35 , 5445, (1994)] |
|
[Tetrahedron Lett. 45 , 3607, (2004)] |