| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
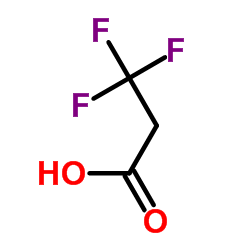 |
3,3,3-Trifluoropropanoic acid
CAS:2516-99-6 |
Yanbin Pan, Tiffany Ayani, Janos Nadas, Shouming Wen, Zhongwu Guo
Index: Carbohydr. Res. 339(12) , 2091-100, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
N-Acetyl-D-neuraminic acid (NeuNAc) aldolase is an important enzyme for the metabolic engineering of cell-surface NeuNAc using chemically modified D-mannosamines. To explore the optimal substrates for this application, eight N-acyl derivatives of D-mannosamine were prepared, and their accessibility to NeuNAc aldolase was quantitatively investigated. The N-propionyl-, N-butanoyl-, N-iso-butanoyl-, N-pivaloyl-, and N-phenylacetyl-D-mannosamines proved to be as good substrates as, or even better than, the natural N-acetyl-D-mannosamine, while the N-trifluoropropionyl and benzoyl derivatives were poor. It was proposed that the electronic effects might have a significant influence on the enzymatic aldol condensation reaction of D-mannosamine derivatives, with electron-deficient acyl groups having a negative impact. The results suggest that N-propionyl-, N-butanoyl-, N-iso-butanoyl-, and N-phenylacetyl-D-mannosamines may be employed to bioengineer NeuNAc on cells.
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
3,3,3-Trifluoropropanoic acid
CAS:2516-99-6 |
C3H3F3O2 |
|
The many roles for fluorine in medicinal chemistry.
2008-08-14 [J. Med. Chem. 51 , 4359-69, (2008)] |
|
Synthesis of ethyl 3,3,3-trifluoropropionate from 2-bromo-3,...
[J. Fluor. Chem. 167 , 135-138, (2014)] |
|
157 nm Resist Materials: A Progress Report. Chiba T, et al.
[J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 13(4) , 657-664, (2000)] |
|
Bi-phobic cellulose fibers derivatives via surface trifluoro...
[Langmuir 23(21) , 10801-10806, (2007)] |
Home | MSDS/SDS Database Search | Journals | Product Classification | Biologically Active Compounds | Selling Leads | About Us | Disclaimer
Copyright © 2026 ChemSrc All Rights Reserved