Effect of retinoids on the growth of squamous cell carcinoma of the palate in rats.
C C Huang
Index: Am. J. Otolaryngol. 7(1) , 55-7, (1986)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The in vivo effects of retinoids on head and neck tumors were studied using Fisher 344 rats with squamous cell carcinoma implanted in the palate. Retinoids were given orally to rats, starting 2 weeks after tumor implantation. The animals were killed at 4 weeks, and the tumor volumes and body weights were measured. The animals had a greater response to all-trans-retinoic acid (58 per cent) and 13-cis-retinoic acid (60 per cent) than to all-trans-retinol (20 per cent) and 13-cis-retinal (30 per cent). Comparison of both tumor volumes and body weights among the retinoid-treated groups revealed that the body weights increased while the tumor volumes decreased. Retinoids seem to inhibit local tumor growth through their effects on host cellular and humoral immunity and through the inhibition of tumor cell keratinization.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
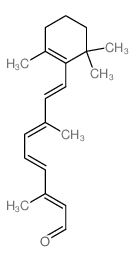 |
Retinal, 13-cis
CAS:472-86-6 |
C20H28O |
|
HEK293S cells have functional retinoid processing machinery.
2002-06-01 [J. Gen. Physiol. 119(6) , 593-612, (2002)] |
|
Probing human red cone opsin activity with retinal analogues...
2011-03-25 [J. Nat. Prod. 74 , 391-4, (2011)] |
|
Cantilever-based sensor for the detection of different chrom...
2007-06-15 [Anal. Chem. 79(12) , 4702-8, (2007)] |
|
In vivo treatment with CPT-11 leads to differentiation of ne...
2004-05-01 [Cancer Res. 64(9) , 3223-9, (2004)] |
|
FTIR study of the photoisomerization processes in the 13-cis...
2006-04-11 [Biochemistry 45(14) , 4362-70, (2006)] |