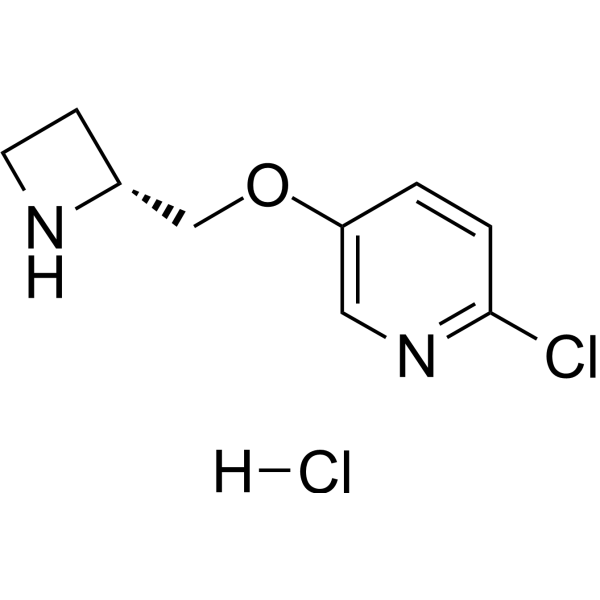
203564-54-9
| Name | 5-[[(2R)-azetidin-2-yl]methoxy]-2-chloropyridine,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII-48U2WUT775
Tebanicline hydrochloride 5-((2R)-2-Azetidinylmethoxy)-2-chloropyridine,hydrochloride Pyridine,5-((2R)-2-azetidinylmethoxy)-2-chloro-,hydrochloride (1:1) ABT-594 hydrochloride Tebanicline (hydrochloride) |
| Description | Tebanicline hydrochloride (ABT594 hydrochloride) is a nAChR modulator with potent, orally effective analgesic activity. It inhibits the binding of cytisine to α4β2 neuronal nAChRs with a Ki of 37 pM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 37 pM (nAChR)[1] |
| In Vitro | Tebanicline is a novel, potent cholinergic nAChR ligand with analgesic properties that shows preferential selectivity for neuronal nAChRs. It inhibits the binding of cytisine to α4β2 neuronal nAChRs with a Ki of 37 pM. Functionally, tebanicline is an agonist. At the transfected human α4β2 neuronal nAChR in K177 cells, with increased 86Rb+ efflux as a measure of cation efflux, ABT-594 has an EC50 value of 140 nM with an intrinsic activitycompared with (−)-nicotine of 130%; at the nAChR subtype expressed in IMR-32 cells, an EC50 of 340 nM; at the F11 dorsal root ganglion cell line, an EC50 of 1220 nM; and via direct measurement of ion currents, an EC50 value of 56,000 nM at the human α7 homo-oligimeric nAChR produced in oocytes[1] |
| In Vivo | Tebanicline is a potent antinociceptive agent with full efficacy in models of acute and persistent pain and that these effects are mediated predominately by an action at central neuronal nAChRs[2]. Tebanicline produces significant antinociceptive effects in mice against both acute noxious thermal stimulation. ABT-594 is orally active, but 10-fold less potent by this route than after i.p. administration. The antinociceptive effect of ABT-594 is prevented, but not reversed, by the noncompetitive neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist[3]. Tebanicline has antinociceptive effects in rat models of acute thermal, persistent chemical, and neuropathic pain. Direct injection of tebanicline into the nucleus raphe magnus (NRM) is antinociceptive in a thermal threshold test and destruction of serotonergic neurons in the NRM attenuates the effect of systemic tebanicline[4]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Rats are dosed with either saline or ABT-594 (0.3 μM/kg i.p.) b.i.d. for 5 days. Treatments are separated by approximately 6 h (i.e., morning and afternoon). In the hot box experiment, animals are tested in the morning and afternoon on days 1, 2 and 5. For each test, a base-line measure is recorded, and then animals are tested 15, 30 and 45 min after treatment. For the afternoon treatment on day 5, all animals received a challenge dose of ABT-594 (0.3 μM/kg i.p.) before being tested. For the motor coordination experiment, animals are tested only in the afternoon on day 5[2]. Mice: Tebanicline is dissolved and diluted in sterile 0.9% saline. The effects of tebanicline are tested for anxiolytic-like activity using the elevated plus-maze procedure. Mice are injected with ABT-594 (0.019, 0.062, or 0.19 μM/kg) or saline, the mouse is placed in the center of the maze and allowed to explore the maze for 5 min. During this period, an auto-mated video tracking system is used to record the time spent on the open arms and the total distance traveled. Diazepam (10.5 μM/kg, i.p). is used as a positive control compound[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12Cl2N2O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 235.11000 |
| Exact Mass | 234.03300 |
| PSA | 34.15000 |
| LogP | 2.60650 |