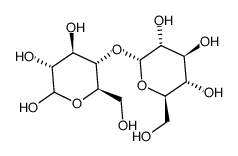
14641-93-1
| Name | Lactose |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
EINECS 238-691-8
MFCD00150747 |
| Description | α-Lactose (α-D-Lactose) is the major sugar present in milk. Lactose exists in the form of two anomers, α and β. The α form normally crystallizes as a monohydrate[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Lactose is a very important sugar because of its abundance in the milk of humans and domestic animals. Lactose is a valuable asset as a basic nutrient and the main substrate in fermentative processes that led to the production of fermented milk products, such as yogurt and kefir[3]. |
| References |
[2]. Lactose. |
| Density | 1.76 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 667.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 201-202ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C12H22O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 342.29600 |
| Flash Point | 357.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 342.11600 |
| PSA | 189.53000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.08E-20mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 52.5 ° (C=10, H2O) |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 1702190000 |
| HS Code | 1702190000 |
|---|