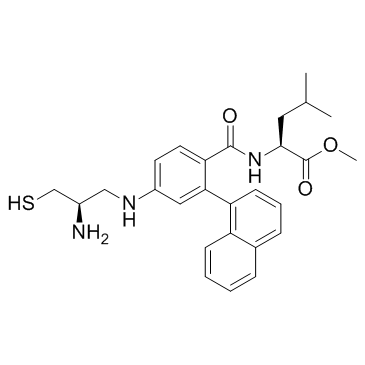
180977-44-0
| Name | methyl (2S)-2-[[4-[[(2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropyl]amino]-2-naphthalen-1-ylbenzoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoate,2,2,2-trifluoroacetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GGTI 298 trifluoroacetate salt hydrate
GGTI-298 trifluoroacetate salt Ggti 298 GGTI-298 GGTI298 |
| Description | GGTI298 is a CAAZ peptidomimetic geranylgeranyltransferase I (GGTase I) inhibitor, strongly inhibiting the processing of geranylgeranylated Rap1A with little effect on processing of farnesylated Ha-Ras, with IC50 values of 3 and > 20 μM in vivo, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 3 μM (Rap1A, in vivo), > 20 μM (Ha-Ras, in vivo)[3] |
| In Vitro | Both RhoA inhibitor (GGTI298) and ROCK inhibitor (H1152) significantly reduce cAMP agonist-stimulated IK(ap), whereas the latter additionally reduces colocalization of KCNN4c with the apical membrane marker wheat germ agglutinin in T84WT cells[1]. Knockdown of DR4 abolishes NF-κB activation, leading to sensitization of DR5-dependent apoptosis induced by the combination of GGTI298 and TRAIL. GGTI298/TRAIL activates NF-κB and inhibits Akt. knockdown of DR5, preventes GGTI298/TRAIL-induced IκBα and p-Akt reduction, suggesting that DR5 mediates reduction of IκBα and p-Akt induced by GGTI298/TRAIL. In contrast, DR4 knockdown further facilitates GGTI298/TRAIL-induced p-Akt reduction[2]. |
| In Vivo | The vivo mouse ileal loop experiments show fluid accumulation is reduced in a dose-dependent manner by TRAM-34, GGTI298, or H1152 when injected together with cholera toxin into the loop[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | The given cells are lysed with Reporter Lysis Buffer and subjected to luciferase activity assay using Luciferase Assay System in a luminometer. Relative luciferase activity is normalized to protein content. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are seeded in 96-well cell culture plates and treated the next day with the agents indicated. The viable cell number is determined using the sulforhodamine B assay. |
| Animal Admin | The ileal loop experiment is performed in 6-8-week-old mice by a modified rabbit ileal loop assay. Following gut sterilization, the animals are kept fasted for 24 h prior to surgery and fed only water ad libitum. Anesthesia is induced by a mixture of ketamine (35 mg/kg of body weight) and xylazine (5 mg/kg of body weight). A laparotomy is performed, and the experimental loops of 5-cm length are constricted at the terminal ileum by tying with non-absorbable silk. The following fluids are instilled in each loop by means of a tuberculin syringe fitted with a disposable needle through the ligated end of the loop as the ligatured is tightened: pure CT (1 μg; positive control), saline (negative control), CT (1 μg) + TRAM-34 (different concentrations in μM as indicated in Fig. 7), CT (1 μg) + H1152 (1 μM), and CT (1 μg) + GGTI298 (different concentrations in μM), a specific inhibitor of Rap1A. The intestine is returned to the peritoneum, and the mice are sutured and returned to their cages. After 6 h, these animals are sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the loops are excised. The fluid from each loop is collected, and the ratio of the amount of fluid contained in the loop with respect to the length of the loop (fluid accumulation ratio in g/cm) is calculated as a reflection of the efficacy of various inhibitors. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C27H33N3O3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 479.63 |
| PSA | 173.04000 |
| LogP | 6.47470 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |