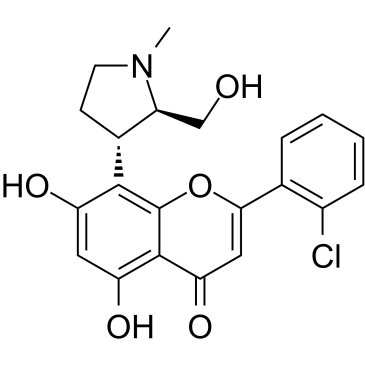
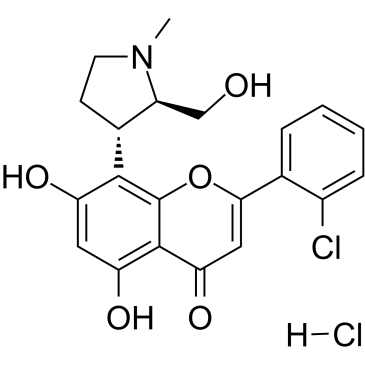
920113-02-6
| Name | 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-[(2S,3R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1-methylpyrrolidin-3-yl]chromen-4-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII-9EK26WE8QN
P 276-00 free base |
| Description | Riviciclib (P276-00 free base) is a potent CDK9-cyclinT1, CDK4-cyclin D1, CDK1-cyclinB, CDK2-cyclin A, CDK2-cyclin E, CDK6-cyclin D3, and CDK9-cyclin H inhibitor with IC50 values of 20 nM, 63 nM, 79 nM, 224 nM, 2500 nM, 396 nM, 2900 nM, respectively[1].Riviciclib shows antitumor activity on cisplatin-resistant cells[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CDK9- Cyclin T1:0.020 μM (IC50) cdk4-cyclin D1:0.063 μM (IC50) CDK1-Cyclin B:0.079 μM (IC50) cdk2-cyclin A:0.224 μM (IC50) cdk2-cyclin E:2.540 μM (IC50) cdk6-cyclin D3:0.396 μM (IC50) CDK9-cyclin H:2.900 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Riviciclib (48 hours; 37°C) is potency against human tumor lines and the IC50s for H-460 cells, MCF-7 cells, HCT-116 cells, HT-29 cells, Colo-205 cells, SW-480 cells, Caco2 cells are 800 nM, 520 nM, 310 nM, 600 nM, 650 nM, 760 nM and 650 nM, respectively, and significantly higher compared with those human tumor cell lines[2]. Riviciclib (3-24 hours; 1.5 μM) reduces cyclin D1, Cdk4, and Rb levels in H-460 cells. Rb (retinoblastoma) phosphorylation at Ser780 decrease at 3 h. Riviciclib (3-24 hours; 1.5 μM) decreases protein levels of cyclin D1 and Cdk4 levels staring at 6 and 9 h in MCF-7 cells, respectively, and accompanied by a decrease in phosphorylation of Rb at Ser780 from 6 h onward, followed by reduced Rb levels at 24 h[2]. Cell Viability Assay[2] Cell Line: HCT-116 cells, HT-29 cells, Colo-205 cells, SW-480 cells, Caco2 cells (Colon carcinoma); U2OS cells (Osteosarcoma); H-4609 cells (Lung carcinoma); HL-60 cells (Promyelocytic); SiHa cells (Cervical carcinoma); MCF-7 cells (Breast carcinoma); PC-3 cells (Prostate carcinoma); T-24 cells (Bladder carcinoma); WI-38 cells, MRC-5 cells (Normal lung fibroblast) Concentration: Incubation Time: 48 hours (37°C) Result: Potency against human tumor lines and the IC50 value for H-460 cells, MCF-7 cells, HCT-116 cells, HT-29 cells, Colo-205 cells, SW-480 cells, Caco2 cells is 800 nM, 520 nM, 310 nM, 600 nM, 650 nM,760 nM and 650 nM, respectively ,and significantly higher compared with those human tumor cell lines[2]. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: H-460 cells; MCF-7 cells Concentration: 1.5 μM Incubation Time: 3, 6, 9, 12, 24 hours Result: Reduced cyclin D1, Cdk4, and Rb levels in H-460 cells. Rb (retinoblastoma) phosphorylation at Ser780 decrease at 3 h. Decreased protein levels of cyclin D1 and Cdk4 levels staring at 6 and 9 h in MCF-7 cells, respectively, and accompanied by a decrease in phosphorylation of Rb at Ser780 from 6 h onward, followed by reduced Rb levels at 24 h. |
| In Vivo | Riviciclib (administered i.p.; 50 mg/kg daily for 20 days, in BALB/c mice) inhibits murine colon cancer (CA-51) growth[3]. Riviciclib (administered i.p.; 30 mg/kg twice daily, every alternate day for 7 days (or 60 mg/kg/d), in BALB/c mice) inhibits murine lung carcinoma model (Lewis lung) growth[3]. Riviciclib (administered i.p.; 35 kg/mg daily for 10 days, in human xenograft mode with severe combined immunodeficient mice) shows significant inhibition in the growth of human colon carcinoma HCT-116 xenograft[3]. Riviciclib (administered via i.p.; 50 mg/kg once daily; 30 mg/kg twice daily for 18 treatments, in human xenograft mode with severe combined immunodeficient mice) significantly inhibits growth[3]. Animal Model: BALB/c mice with murine colon cancer (CA-51)[3] Dosage: 50 mg/kg Administration: Given i.p.; every day for 20 days Result: Growth inhibition of murine colon cancer (CA-51) was significant. Animal Model: BALB/c mice with murine lung carcinoma model (Lewis lung)[3] Dosage: 35 mg/kg; 30 mg/kg twice daily (or 60 mg/kg/d) Administration: Administered i.p.; 35 mg/kg daily for 14 days; Administered i.p.; 30 mg/kg twice daily (or 60 mg/kg/d) everyalternate day for 7 days Result: Given 60 mg/kg (30 mg/kg twice daily) for 7 days was more efficacious, showed significant inhibition in the growth. Animal Model: Human xenograft mode with HCT-116 tumor model (severe combined immunodeficient mice)[3] Dosage: 35 mg/kg Administration: Administered i.p.; daily for 10 days Result: Given 35 mg/kg showed significant inhibition in the growth. Animal Model: Human xenograft model with H-460 tumor xenograft (severe combined immunodeficient mice)[3] Dosage: 50 mg/kg; 30 mg/kg Administration: Administered i.p.; 50 mg/kg once daily for 20 days; Administered i.p.; 30 mg/kg twice daily for 18 treatments Result: Given 50 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg twice daily significantly inhibited growth. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C21H20ClNO5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 401.84 |
| Exact Mass | 401.10300 |
| PSA | 94.14000 |
| LogP | 3.24250 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |