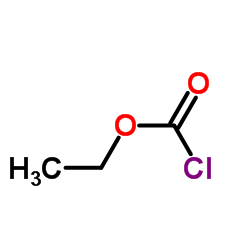
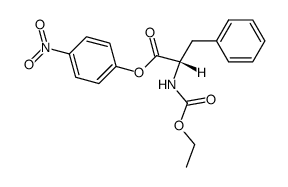
19887-32-2
| Name | n-ethoxycarbonyl-l-phenylalanine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2(S)-N-(ethoxycarbonyl)phenylalanine
(S)-N-(Ethoxycarbonyl)phenylalanine N-Ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenyl-L-alanine N-(ethoxycarbonyl)-L-phenylalanine (ethoxycarbonyl)-L-phenylalanine MFCD00239447 N-Ethoxycarbonyl-L-phenylalanine ETOC-PHE-OH (ethoxycarbonyl)phenylalanine |
| Description | N-Ethoxycarbonyl-L-phenylalanine is a phenylalanine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.213g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 419ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 78-82ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C12H15NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 237.25200 |
| Flash Point | 207.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 237.10000 |
| PSA | 75.63000 |
| LogP | 1.81930 |
| Vapour Pressure | 9.06E-08mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.538 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|
|
~96% 
19887-32-2 |
| Literature: Xu, Qianyong; Yang, Hongfang; Pan, Xinfu; Chan, Albert S.C. Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 2002 , vol. 13, # 9 p. 945 - 951 |
|
~83% 
19887-32-2 |
| Literature: Kita, Yasuyuki; Haruta, Jun-ichi; Tagawa, Hiroko; Tamura, Yasumitsu Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1980 , vol. 45, # 22 p. 4519 - 4522 |
|
~% 
19887-32-2 |
| Literature: Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, , vol. 111, # 11 p. 459 - 468 |
|
~% 
19887-32-2 |
| Literature: Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, , vol. 112, # 1 p. 1 - 6 |
|
~% 
19887-32-2
Detail
|
| Literature: Chemistry Letters, , vol. 41, # 1 p. 42 - 43 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |