72957-38-1
| Name | Dynorphin A (1-13) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII:VFC23V742Z
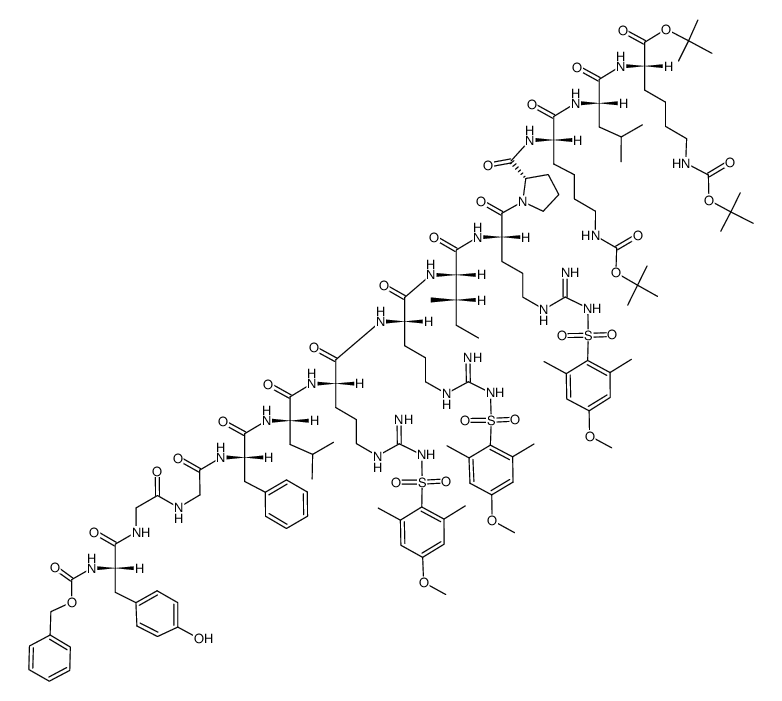
dynorphin A-(1-13) DYNORPHIN 1-13 DYNORPHIN A (1-13),PORCINE dyn A-(1-13)-OH L-Tyrosylglycylglycyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-leucyl-L-arginyl-L-arginyl-L-isoleucyl-L-arginyl-L-prolyl-L-lysyl-L-leucyl-L-lysine DYNORPHIN A(HUMAN,1-13) YGGFLRRIRPKLK Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys Dyn(1-13) DYNORPHIN A PORCINE FRAGMENT 1-13 Dynorphin A (1-13) Acetate Porcine dynorphin A(1-13) |
| Description | Porcine dynorphin A (1-13) is a potent, endogenous κ opioid receptor agonist and is antinociceptive at physiological concentrations. Sequence: Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Κ opioid receptor[1]. |
| In Vivo | Dynorphin A (1-13) exposure (33 μM) causes a significant loss in neuronal viability at 4 h with a visible destruction in neuronal morphology seen at 16 h. Exposure to dynorphin A (1-13) causes acute increases in [Ca2+]i in individual neurons similar to increases seen with acute NMDA treatment. Continuous exposure to dynorphin A (1-13) (100 μM) causes a significant loss of neurons over time[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C75H126N24O15 |
| Molecular Weight | 1603.955 |
| Exact Mass | 1602.983398 |
| PSA | 661.70000 |
| LogP | -0.50 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.645 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~57% 
72957-38-1 |
| Literature: Wakimasu; Kitada; Fujino Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1981 , vol. 29, # 9 p. 2592 - 2597 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |