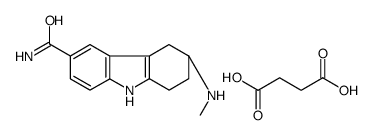
158930-09-7
| Name | butanedioic acid,(6R)-6-(methylamino)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-carbazole-3-carboxamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Frovatriptan succinate anhydrous
UNII-36K05YF32G Frovatriptan Succinate |
| Description | Frovatriptan succinate ((R)-Frovatriptan succinate) is a potent, high affinity, selective and orally active 5-HT1B (pK50 of 8.2) and 5-HT1D receptor agonist. Frovatriptan succinate exhibits >10-fold selectivity for 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D over 5-HT1A, 5-HT1F, and 5-HT7 and >1000-fold selectivity over other 5-HT, dopamine, histamine H1, and α1-adrenoceptor. Frovatriptan succinate has the potential for migraine research[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
5-HT1B Receptor:8.2 (pEC50) 5-HT1D Receptor |
| In Vitro | Cerebral vasodilatation and neurogenic inflammation are considered to be prime movers in the pathogenesis of migraine. Activation of 5-HT1B reverses cerebral vasodilatation and activation of 5-HT1D prevents neurogenic inflammation. Frovatriptan has a high affinity for 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors and a moderate affinity for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1F receptors subtypes. Frovatriptan has a moderate affinity for the 5-HT7 receptors, an action associated with coronary artery relaxation in the dog[1]. |
| In Vivo | Oral bioavailability of Frovatriptan is 22%-30% and is not affected by food. Although the maximum concentration in the plasma is achieved in 2-3 hours, 60%-70% of this is achieved in 1 hour. A steady state is achieved in 4-5 days. Plasma protein binding is low at 15%. The most unique feature is the relative terminal long half-life of about 26 hours. Frovatriptan is chiefly metabolized by CYP1A2 and is cleared by the kidney and liver making moderate failure of either organ not a limiting factor in treatment[1]. Frovatriptan (0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 mg/kg; a single bolus intraduodenal administration) treatment produces an increase in carotid vascular resistance, which is sustained for at least 5 hours in dogs[2]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 515.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H23N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 361.39200 |
| Flash Point | 265.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 361.16400 |
| PSA | 146.50000 |
| LogP | 2.55440 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.01E-10mmHg at 25°C |