BIX02189
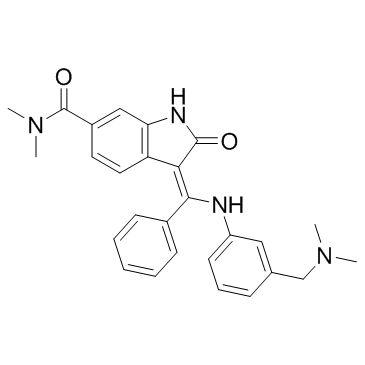
BIX02189 structure
|
Common Name | BIX02189 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1265916-41-3 | Molecular Weight | 440.537 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 653.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H28N4O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 349.0±31.5 °C | |
Use of BIX02189BIX02189 is a potent and selective MEK5 inhibitor with an IC50 of 1.5 nM. BIX02189 also inhibits ERK5 catalytic activity with an IC50 of 59 nM. |
| Name | BIX02189 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | BIX02189 is a potent and selective MEK5 inhibitor with an IC50 of 1.5 nM. BIX02189 also inhibits ERK5 catalytic activity with an IC50 of 59 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
MEK5:1.5 nM (IC50) ERK5:59 nM (IC50) CSF1R (FMS):46 nM (IC50) LCK:250 nM (IC50) JAK3:440 nM (IC50) TGFβR1:580 nM (IC50) RPS6KA6 (RSK4):990 nM (IC50) RPS6KA3 (RSK2):2.1 μM (IC50) FGFR1:1 μM (IC50) KIT:1.1 μM (IC50) ABL1:2.4 μM (IC50) MAPK14 (p38 alpha):3.7 μM (IC50) SRC:7.6 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | BIX02189 blocks phosphorylation of ERK5, without affecting phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in sorbitol-stimulated HeLa cells. BIX02189 inhibits ERK5 phosphorylation in a dose dependent manner[1]. Fluvastatin reduces advanced glycation endproduct (AGE)-induced vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) proliferation. To confirm this effect, VSMCs are treated with AGEs in the presence or absence of Fluvastatin and then subject to MTT assay. AGEs are found to dose-dependently induce cell proliferation, and this is significantly suppressed by Fluvastatin. In addition to MTT assay, the similar results are got with cell counting. This suppressive effect of Fluvastatin is prevented when VSMCs are pretreated with BIX02189. Whether ERK5 activation can reduce proliferation is also examined by using Ad-CA-MEK5α encoding a constitutively active mutant form of MEK5α (an upstream kinase of ERK5). AGE-induced proliferation determined by both MTT assay and cell counting is significantly diminished in the presence of Ad-CA-MEK5α, and Nrf2 depletion using siRNA restored AGE-induced proliferation[2]. |
| In Vivo | Mice are treated with either 10 mg/kg of BIX02189 (in 25% DMSO) or vehicle control (same volume of 25% DMSO) by intraperitoneal injection. The nuclear localization of Nrf2 is inhibited in aortic endothelial cells from mice treated with BIX02189[3]. |
| Cell Assay | AGE-induced proliferation is quantified using the MTT assay. Briefly, VSMCs are cultured on 24-well plates and when ~80% confluent, medium is replaced with serum free DMEM. Cells are then pretreated with BIX02189 (2 μM) and stimulated with Fluvastatin (5 μM) for 24 h. MTT reagents are added for 4 h at 37°C the removed by washing with PBS, and eluted with DMSO. Proliferation is measured using a microplate reader at 570 nm[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] C57BL/6-specific pathogen-free mice are used. To determine the role of ERK5 on laminar flow-dependent Nrf2 nuclear translocation in vivo, 6-week-old male C57BL/6 mice are intraperitoneally treated with BIX02189 (10 mg/kg of body weight in 25% DMSO) or vehicle control. Following euthanization, vascular perfusion is performed with saline for 5 min followed by fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde for 5 min. Isolated aorta is incubated with 0.1% PBS with Tween, and then fat is removed. 5% goat serum is used for blocking and antibody diluents. Aortic endothelial cells are stained with anti-vascular endothelial-cadherin antibody and Topro3 for endothelial cell junction and nuclear, respectively. Cellular localization of Nrf2 is determined by immunofluorescence staining with anti-Nrf2 antibody under the Confocal microscope[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 653.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C27H28N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 440.537 |
| Flash Point | 349.0±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 440.221222 |
| LogP | 2.05 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.659 |
| InChIKey | ZGXOBLVQIVXKEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CN(C)Cc1cccc(N=C(c2ccccc2)c2c(O)[nH]c3cc(C(=O)N(C)C)ccc23)c1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| MFCD18074528 |
| 1H-Indole-6-carboxamide, 3-[[[3-[(dimethylamino)methyl]phenyl]amino]phenylmethylene]-2,3-dihydro-N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-, (3Z)- |
| (3Z)-3-[({3-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]phenyl}amino)(phenyl)methylene]-N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-6-indolinecarboxamide |