Pyridoxatine
Modify Date: 2024-01-06 15:59:07
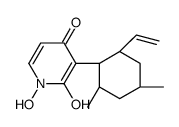
Pyridoxatine structure
|
Common Name | Pyridoxatine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 135529-30-5 | Molecular Weight | 263.33200 | |
| Density | 1.245g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 393.5ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 191.8ºC | |
Use of PyridoxatinePyridoxatin is a free radical scavenger of microbial origin. Pyridoxatin is isolated from a fungus culture identified as Acremonium sp. BX86. Pyridoxatin inhibits lipid peroxidation induced by free radicals in rat liver microsomes free from vitamin E[1]. |
| Name | pyridoxatin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pyridoxatin is a free radical scavenger of microbial origin. Pyridoxatin is isolated from a fungus culture identified as Acremonium sp. BX86. Pyridoxatin inhibits lipid peroxidation induced by free radicals in rat liver microsomes free from vitamin E[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.245g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 393.5ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 263.33200 |
| Flash Point | 191.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 263.15200 |
| PSA | 62.46000 |
| LogP | 2.74300 |
| Vapour Pressure | 7.99E-08mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.627 |
| 3-[(1S,2R,4S,6R)-2-ethenyl-4,6-dimethylcyclohexyl]-1,4-dihydroxypyridin-2-one |
| 3-[(1S,2R,4S,6R)-2-ethenyl-4,6-dimethylcyclohexyl]-1,2-dihydroxypyridin-4-one |
| 2(1H)-Pyridinone,3-(2-ethenyl-4,6-dimethylcyclohexyl)-1,4-dihydroxy-,(1alpha,2beta,4beta,6beta) |