Volinanserin
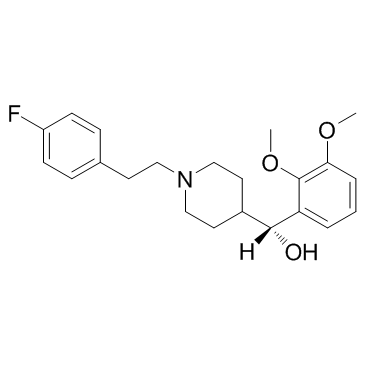
Volinanserin structure
|
Common Name | Volinanserin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 139290-65-6 | Molecular Weight | 373.461 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 499.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H28FNO3 | Melting Point | 89-91ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 255.8±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of VolinanserinVolinanserin is a potent and selective antagonist of 5-HT2 receptor, with a Ki of 0.36 nM, and shows 300-fold selectivity for 5-HT2 receptor over 5-HT1c, alpha-1 and DA D2 receptors. Volinanserin has antipsychotic activity. |
| Name | volinanserin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Volinanserin is a potent and selective antagonist of 5-HT2 receptor, with a Ki of 0.36 nM, and shows 300-fold selectivity for 5-HT2 receptor over 5-HT1c, alpha-1 and DA D2 receptors. Volinanserin has antipsychotic activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 0.36 nM (5-HT2 receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | Volinanserin (MDL 100907) is a potent antagonist at the 5-HT2 receptor, with a Ki of 0.36 nM, and shows 300-fold selectivity for 5-HT2 receptor over 5-HT1c receptor, alpha-1 and DA D2 receptors. Volinanserin has antipsychotic activity[1]. |
| In Vivo | Volinanserin (MDL 100907; 0.008-2.0 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly decreases d-amphetamine-stimulated locomotor activity in mice, with an ED50 of 0.3 mg/kg, but shows no obvious reduction in the base-line locomotor activity in mice. Volinanserin produces atalepsy with an ED50 of 10-50 mg/kg in rats. Volinanserin does not reduces apomorphine-induced stereotypies or produces catalepsy in rats[1]. Volinanserin (M100907) combined with MK-801 significantly decreases reinforcers at 1 μg/kg, but dose-dependently (10, 100 μg/kg) antagonizes the disruptive effect of MK-801 in rats via i.p. administration. Volinanserin (6.25 μg/kg) enhances the antidepressant-like action of desipramine in rats performing under a DRL 72-s schedule, and elevates the antidepressant-like effect of tranylcypromine[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] To measure the effects the test compounds alone on spontaneous locomotor activity, mice are injected i.p. with the test compounds, placed singly into clear Plexiglas test cages (16 × 16 × 8 inches) and are allowed to acclimatize for 30 mm. Six mice per dose for each of the six doses are tested for Volinanserin (0.008-2.0 mg/kg), amperozide and haloperidol. Twelve mice per dose for six doses are tested for clozapine. Sixty animals are given vehicle in these experiments. Thereafter, the boxes are placed in the activity monitors and measurements are taken for 30 mm. To measure the effects of various pretreatments on amphetamine stimulated motor activity, mice (four per test box) are acclimatized for 90 mm to reduce the level of spontaneous activity of the controls. The mice are then injected with amphetamine (2 mg/kg i.p.) as well as the test compounds, returned to the activity boxes and tested for 90 mm. In these experiments 16 mice per dose are tested for the 9 doses of Volinanserin and 16 mice per dose are tested for each of 6 doses for amperozide, clozapine and haloperidol. One hundred forty four mice received vehicle in these experiments[1]. Rats[1] Drugs and doses used are clozapine (1, 10 and 50 mg/kg) or Volinanserin (1, 10 and 50 mg/kg), amperozide (1, 10 and 50 mg/kg) and haloperidol (0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg). Five rats per dose are used in these experiments and five rats receive vehicle. Rats are dosed i.p. and, 30 mm later, each rat is placed gently into a clear Plexiglas enclosure (30 × 30 × 15 cm) so that both front limbs rested on top of a horizontal aluminum rod (1.2 cm in diameter). The rod is centered across the plastic enclosure at a height of 7 cm above the floor. The time each rat remained with its hind legs on the floor while the front limbs are elevated on the rod is recorded to the nearest second. Data are analyzed by using analysis of variance followed by appropriate post-hoc tests[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 499.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 89-91ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H28FNO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 373.461 |
| Flash Point | 255.8±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 373.205322 |
| PSA | 41.93000 |
| LogP | 3.56 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.557 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Activation of serotonin2A receptors in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca complex enhanced working memory in the hemiparkinsonian rats.
Neuropharmacology 91 , 23-33, (2015) Serotonin2A (5-HT2A) receptors are highly expressed in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca complex (MS-DB), especially in parvalbumin (PV)-positive neurons linked to hippocampal theta rhythm, whi... |
|
|
Serotonin 2A receptor antagonists for treatment of schizophrenia.
Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 20(9) , 1211-23, (2011) All approved antipsychotic drugs share an affinity for the dopamine 2 (D(2)) receptor; however, these drugs only partially ameliorate the symptoms of schizophrenia. It is, therefore, of paramount impo... |
|
|
Involvement of 5-HT2A receptor and α2-adrenoceptor blockade in the asenapine-induced elevation of prefrontal cortical monoamine outflow.
Synapse 66(7) , 650-60, (2012) The psychotropic drug asenapine is approved for the treatment of schizophrenia and manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder. Asenapine exhibits higher affinity for several 5-HT recep... |
| (R)-(2,3-Dimethoxyphenyl){1-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]-4-piperidinyl}methanol |
| (R)-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl){1-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]piperidin-4-yl}methanol |
| Volinanserin Hydrochloride Salt |
| MDL-100,907 |
| Volinanserin |
| 4-Piperidinemethanol, α-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]-, (αR)- |