dl-methioninol
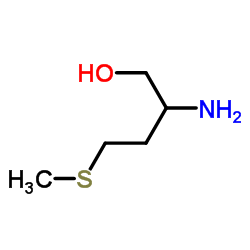
dl-methioninol structure
|
Common Name | dl-methioninol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16720-80-2 | Molecular Weight | 135.228 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 270.2±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H13NOS | Melting Point | 31ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 117.2±24.6 °C | |
| Name | 2-amino-4-methylsulfanylbutan-1-ol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 270.2±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 31ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H13NOS |
| Molecular Weight | 135.228 |
| Flash Point | 117.2±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 135.071777 |
| PSA | 71.55000 |
| LogP | -0.11 |
| Appearance of Characters | viscous liquid |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.516 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Methionine and its derivatives increase bladder excitability by inhibiting stretch-dependent K+ channels. Baker, S.A. et al.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 53 , 1259-1271, (2008)
|
|
|
Redox inversion of helicity in propeller-shaped molecules derived from s-methyl cysteine and methioninol.
Org. Lett. 5(5) , 709-11, (2003) One-electron reduction inverts the helicity of copper complexes formed from derivatives of S-methylcysteine and methioninol. The change in conformation of the organic ligand is followed in the exciton... |
|
|
Methionine and its derivatives increase bladder excitability by inhibiting stretch-dependent K(+) channels.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 153(6) , 1259-71, (2008) During the bladder filling phase, the volume of the urinary bladder increases dramatically, with only minimal increases in intravesical pressure. To accomplish this, the smooth muscle of the bladder w... |
| 2-Amino-4-(methylthio)-1-butanol |
| D-methioninol |
| 1-Butanol, 2-amino-4-(methylthio)- |
| MFCD00068312 |
| DL-METHIONOL |
| 2-amino-4-(methylsulfanyl)butan-1-ol |
| DL-Methioninol |
| 4-METHYLMERCAPTO-2-AMINO-1-BUTANOL |
| L-2-amino-4-methylsulfanylbutanol |
| 2-Amino-4-(methylsulfanyl)-1-butanol |
| 2-azanyl-4-methylsulfanyl-butan-1-ol |
| H-DL-MET-OL |

