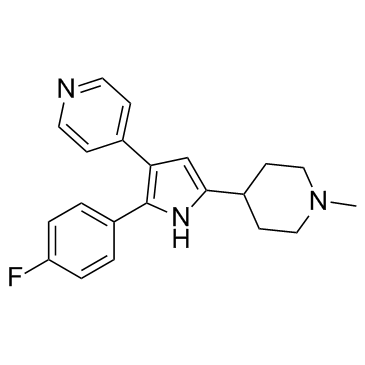
| Description |
MBP146-78 is a potent and selective inhibitor of cGMP dependent protein kinases.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| In Vitro |
MBP146-78 displays a dose-dependent inhibition of T. gondii tachyzoites replicating inside HFFs, with an IC50 of 210 nM. The suppression of lytic parasite growth by MBP146-78 is reversible. Replacement of the medium with medium lacking MBP146-78, after treatment for up to 7 days at 2 μM, results in complete lysis of HFF cell monolayers. MBP146-78 is neither toxic nor inhibitory to proliferating or confluent monolayers of HFFs at concentrations of up to 10 μM[1].
|
| In Vivo |
In infected mice that are treated with MBP146-78 at 50 mg/kg twice daily, parasites are undetectable throughout the 10-day treatment period in each of the tissues examined. However, samples from brain, spleen, and lung taken from infected treated mice reveal the presence of parasites after cessation of administration of MBP146-78, indicating that a transient asymptomatic parasite recrudescence occurs in all survivors. The ability of mice to control Toxoplasma infection after MBP146-78 treatment has been terminated suggests that the mouse immune system plays a synergistic role with chemotherapy in controlling the infection[1].
|
| Cell Assay |
To assess the toxicity of MBP146-78 to HFFs, cells are plated in 96-well plates at 1000/well and allowed to adhere overnight prior to addition of compound. Cultures are incubated for 5 days at 37°C in the presence of 5% CO2. Viability is assessed using the Cell-Titer 96 Aqueous One solution cell-proliferating assay[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Mice: MBP146-78 is dissolved in water. MBP146-78 is administered in 100 μL doses by intraperitoneal injections starting 24 h after parasite inoculation. Mice are monitored twice daily for clinical evidence of toxoplasmosis and mortality throughout the experimental period[1].
|
| References |
[1]. Nare B, et al. Evaluation of a cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor in treatment of murine toxoplasmosis: gamma interferon is required for efficacy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Feb;46(2):300-7.
|