Abscisic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 17:39:27
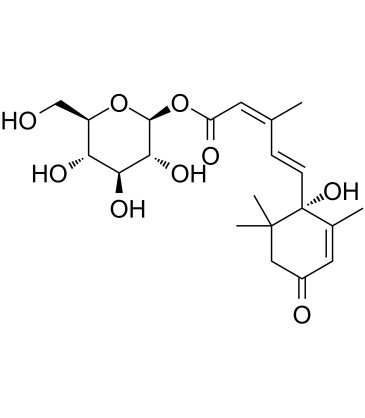
Abscisic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl ester structure
|
Common Name | Abscisic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl ester | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21414-42-6 | Molecular Weight | 426.46 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H30O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Abscisic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl esterβ-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate (ABA-GE) is a hydrolyzable abscisic acid (ABA) conjugate that accumulates in the vacuole and presumably also in the endoplasmic reticulum. The deconjugation of β-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate allows the rapid formation of free ABA in response to abiotic stress conditions such as dehydration and salt stress. β-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate contributes to the maintenance of ABA homeostasis[1]. |
| Name | β-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate |
|---|
| Description | β-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate (ABA-GE) is a hydrolyzable abscisic acid (ABA) conjugate that accumulates in the vacuole and presumably also in the endoplasmic reticulum. The deconjugation of β-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate allows the rapid formation of free ABA in response to abiotic stress conditions such as dehydration and salt stress. β-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate contributes to the maintenance of ABA homeostasis[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Deconjugation of β-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate (ABA-GE) by the endoplasmic reticulum and vacuolar β-glucosidases allows the rapid formation of free ABA in response to abiotic stress conditions such as dehydration and salt stress. β-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate further contributes to the maintenance of ABA homeostasis, as it is the major ABA catabolite exported from the cytosol. Vacuolar transport ofβ-D-Glucopyranosyl abscisate is mediated by ATP-binding cassette and proton-antiport mechanisms in arabidopsis[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C21H30O9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 426.46 |
| InChIKey | HLVPIMVSSMJFPS-VTEUUMMASA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C=CC1(O)C(C)=CC(=O)CC1(C)C)=CC(=O)OC1OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C1O |