Dimaprit dihydrochloride
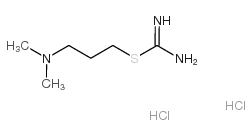
Dimaprit dihydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Dimaprit dihydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23256-33-9 | Molecular Weight | 234.19000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H17Cl2N3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Dimaprit dihydrochlorideDimaprit dihydrochloride is a selective histamine H2 receptor agonist, it also inhibits nNOS with an IC50 of 49 μM. Dimaprit dihydrochloride can stimulate gastric acid secretion[1][2]. |
| Name | Dimaprit dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dimaprit dihydrochloride is a selective histamine H2 receptor agonist, it also inhibits nNOS with an IC50 of 49 μM. Dimaprit dihydrochloride can stimulate gastric acid secretion[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
H2 Receptor nNOS:49 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Dimaprit has less than 0.0001% the activity of histamine on H1-receptors[1]. Dimaprit (0.1 nM-100 μM) inhibits nNOS concentration dependently with an IC50 of 49±14 μM[2]. |
| In Vivo | Dimaprit stimulates gastric acid secretion in rats (1.25 μM/kg/min; rapid i.v. injection), cats (2-64 μM/h; i.v.) and dogs (1-100 nM/kg/min; i.v.)[1]. Dimaprit (0.01-1 μM/kg; i.v. at intervals of 5 min) causes dose-dependent falls in blood pressure in cats. Dimaprit (1-100 nM; intra-arterial injection) causes vasodilatation in the femoral vascular bed, and it (1 μM/kg; bolus or intravenous injection) has no effect on heart rate[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C6H17Cl2N3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 234.19000 |
| Exact Mass | 233.05200 |
| PSA | 78.41000 |
| LogP | 2.96880 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Endothelial CD99 signals through soluble adenylyl cyclase and PKA to regulate leukocyte transendothelial migration.
J. Exp. Med. 212 , 1021-41, (2015) CD99 is a critical regulator of leukocyte transendothelial migration (TEM). How CD99 signals during this process remains unknown. We show that during TEM, endothelial cell (EC) CD99 activates protein ... |
|
|
Involvement of histaminergic inputs in the jaw-closing reflex arc.
J. Neurophysiol. 113 , 3720-35, (2015) Histamine receptors are densely expressed in the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (MesV) and trigeminal motor nucleus. However, little is known about the functional roles of neuronal histamine in cont... |
|
|
Analysis of the histamine H2-receptor in human monocytes.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 92(2) , 369-79, (2014) Histamine receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Canonically, the histamine H2-receptor (H2R) couples to Gs-proteins and activates adenylyl cyclases (ACs) with subsequent adenosine-3',5'-c... |
| S-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)isothiourea dihydrobromide |
| Carbamimidothioic acid (3-(dimethylamino)propyl ester |
| 3-(dimethylamino)propyl carbamimidothioate,dihydrochloride |