L-4-Nitrophenylalanine
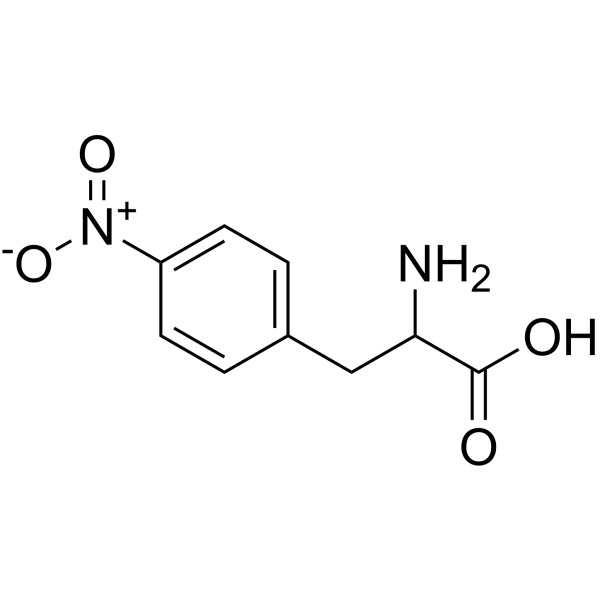
L-4-Nitrophenylalanine structure
|
Common Name | L-4-Nitrophenylalanine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2922-40-9 | Molecular Weight | 210.187 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 414.1±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10N2O4 | Melting Point | 236-237 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 204.2±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of L-4-NitrophenylalanineH-DL-Phe(4-NO2)-OH is a phenylalanine derivative[1]. |
| Name | p-nitro-dl-phenylalanine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | H-DL-Phe(4-NO2)-OH is a phenylalanine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 414.1±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 236-237 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 210.187 |
| Flash Point | 204.2±25.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 210.064056 |
| PSA | 109.14000 |
| LogP | 0.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.614 |
| InChIKey | GTVVZTAFGPQSPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(Cc1ccc([N+](=O)[O-])cc1)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R25 |
| Safety Phrases | S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
|
Sensitive, soluble chromogenic substrates for HIV-1 proteinase.
J. Biol. Chem. 265 , 7733, (1990) By replacement of the P1' residue in a capsid/nucleocapsid cleavage site mimic with 4-NO2-phenylalanine (Nph), an excellent chromogenic substrate, Lys-Ala-Arg-Val-Leu*Nph-Glu-Ala-Met, for HIV-1 protei... |
|
|
Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
PLoS ONE 5(2) , e9354, (2010) New tools are needed to study the intracellular pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the causative agent of tuberculosis (TB), to facilitate new drug discovery and vaccine development. We have d... |
|
|
Comparison of fluorescence reagents for simultaneous determination of hydroxylated phenylalanine and nitrated tyrosine by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection.
Biomed. Chromatogr. 26(1) , 41-50, (2012) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are well-known and important contributors to oxidative and nitrosative stress in several diseases. Hydroxylated phenylalanine and nitr... |
| 2-Amino-3-(4-nitrophenyl)propanoic acid |
| 4-nitro-DL-phenylalanine |
| L-4-Nitrophe |
| 4-Nitrophenylalanine |
| para-nitrophenylalanine |
| L-Phenylalanine, 4-nitro- (9CI) |
| p-Nitrophenylalanine |
| L-Phenylalanine, 4-nitro- |
| Nitrophenylalanine |
| 4-14-00-01677 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) |
| DL-phenylalanine, 4-nitro- |
| L-p-Nitrophenylalanine |
| 4-Nitro-DL-phenylalanine hydrate |
| EINECS 220-868-6 |
| L-Phe(4-NO2)-OH |
| Alanine, 3-(p-nitrophenyl)-, L- |
| L-4- Nitrophenylalanine |
| 3-(4-Nitrophenyl)-L-alanine |
| dl-p-Nitrophenylalanine |
| 4-NITRO-DL-PHE-OH |
| 4-NITRO-L-PHENYLANINEHYDRATE |
| H-P-NITRO-DL-PHE-OH |
| MFCD00007384 |
| 4-nitro Phenylalanine |
| Phenylalanine, 4-nitro- |
| DL-4-NO2-Phe-OH |
| p-Nitrophenylalanine, DL- |
| (2S)-2-amino-3-(4-nitrophenyl)propanoic acid |
| P-NITRO-DL-PHENYLALA |

