Ethambutol
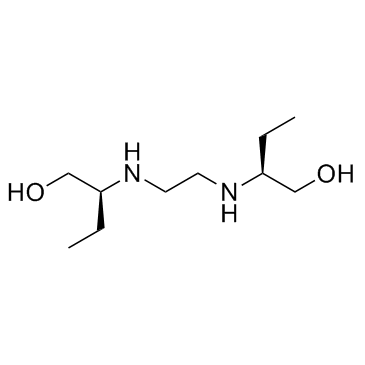
Ethambutol structure
|
Common Name | Ethambutol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 74-55-5 | Molecular Weight | 204.310 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 345.3±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H24N2O2 | Melting Point | 199 - 204ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 113.7±12.9 °C | |
Use of EthambutolEthambutol is a bacteriostatic antimycobacterial agent, which obstructs the formation of cell wall by inhibiting arabinosyl transferases.Target: AntibacterialEthambutol directly affects two polymers, arabinogalactan (AG) and lipoarabinomannan (LAM) in Mycobacterium smegmatis. In M. smegmatis, Ethambutol inhibits synthesis of arabinan completely and inhibits AG synthesis most likely as a consequence of this; more than 50% of the cell arabinan is released from the bacteria following Ethambutol treatment, whereas no galactan is released. Ethambutol main targets against embB gene product in M. avium. Ethambutol induces 60% changes in the embB gene in M. tuberculosis resistant mutants [1]. Ethambutol is effective against actively growing microorganisms of the genus Mycobacterium, including M. tuberculosis. Nearly all strains of M. tuberculosis and M. kansasii as well as a number of strains of the M. aviumcomplex (MAC) are sensitive to Ethambutol. [1] Ethambutol is potency against M. tuberculosis (H37Rv) with MIC of 0.5 μg/mL in vitro [2]. Ethambutol is efficient on treatment of mycobacterial-infected macrophages. When M. tuberculosis infected macrophages are treated with 6 μg/mL Ethambutol, the log CFUs following treatment for 3 days is 4.17, while value in control group is 4.8. The MICs for M. avium (MTCC 1723) and M. smegmatis (MTCC 6) are 15 μg/mL and 0.18 μg/mL, respectively. Ethambutol is efficient in animal model. 100 mg/kg Ethambutol given orally 15 days post i.v. infection 1 ×/week for 5 weeks, induces a lower log CFU compared with untreatment (4.59 vs 5.07) [3]. |
| Name | ethambutol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ethambutol is a bacteriostatic antimycobacterial agent, which obstructs the formation of cell wall by inhibiting arabinosyl transferases.Target: AntibacterialEthambutol directly affects two polymers, arabinogalactan (AG) and lipoarabinomannan (LAM) in Mycobacterium smegmatis. In M. smegmatis, Ethambutol inhibits synthesis of arabinan completely and inhibits AG synthesis most likely as a consequence of this; more than 50% of the cell arabinan is released from the bacteria following Ethambutol treatment, whereas no galactan is released. Ethambutol main targets against embB gene product in M. avium. Ethambutol induces 60% changes in the embB gene in M. tuberculosis resistant mutants [1]. Ethambutol is effective against actively growing microorganisms of the genus Mycobacterium, including M. tuberculosis. Nearly all strains of M. tuberculosis and M. kansasii as well as a number of strains of the M. aviumcomplex (MAC) are sensitive to Ethambutol. [1] Ethambutol is potency against M. tuberculosis (H37Rv) with MIC of 0.5 μg/mL in vitro [2]. Ethambutol is efficient on treatment of mycobacterial-infected macrophages. When M. tuberculosis infected macrophages are treated with 6 μg/mL Ethambutol, the log CFUs following treatment for 3 days is 4.17, while value in control group is 4.8. The MICs for M. avium (MTCC 1723) and M. smegmatis (MTCC 6) are 15 μg/mL and 0.18 μg/mL, respectively. Ethambutol is efficient in animal model. 100 mg/kg Ethambutol given orally 15 days post i.v. infection 1 ×/week for 5 weeks, induces a lower log CFU compared with untreatment (4.59 vs 5.07) [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[1]. Ethambutol. Tuberculosis (Edinb), 2008. 88(2): p. 102-5. |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 345.3±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 199 - 204ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H24N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 204.310 |
| Flash Point | 113.7±12.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 204.183777 |
| PSA | 64.52000 |
| LogP | -0.05 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.478 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| HS Code | 2922191000 |
|---|
|
~% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 122, # 25 p. 5968 - 5976 |
|
~% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 122, # 25 p. 5968 - 5976 |
|
~78% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Kotkar, Shriram P.; Sudalai, Arumugam Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 2006 , vol. 17, # 11 p. 1738 - 1742 |
|
~% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Doklady Chemistry, , vol. 145, p. 597 - 600 Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, , vol. 145, p. 332 - 335 |
|
~% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , p. 1455 - 1464 |
|
~% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , p. 1455 - 1464 |
|
~% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 58, # 49 p. 9765 - 9767 |
|
~% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 83, p. 2212 - 2213 |
|
~% 
Ethambutol CAS#:74-55-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, , vol. 5, p. 835 - 845 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2922191000 |
|---|
| (S,S)-Et,Et-FerroTANE |
| (+)-1,1'-BIS[(2R,4R)-2,4-DIETHYLPHOSPHONATO]FERROCENE |
| R,R-Et-FerroTANE |
| (S,S)-2,2'-(ethylenediimino)di-1-butanol |
| (R,R)-ET-FERROTANE(TM) |
| (+)-1,1'-BIS((2R,4R)-2,4-DIETHYLPHOSPHOTANO)FERROCENE |
| (S,S)-1-[1-(DI-TERT-BUTYLPHOSPHINO)ETHYL]-2-(DIPHENYLPHOSPHINO)FERROCENE |
| Et-Ferrotane |
| 1-Butanol, 2,2'-(1,2-ethanediyldiimino)bis- |
| Ethambutol |
| (S)-(+)-1-[(R)-2-(DIPHENYLPHOSPHINO)FERROCENYL]ETHYLDI-T-BUTYLPHOSPHINE |
| 2,2'-(1,2-Ethanediyldiimino)di(1-butanol) |
| JOSIPHOS SL-J002-2 |
![N,N'-bis[(2S)-1-[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxybutan-2-yl]oxamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/141/909567-52-8.png)
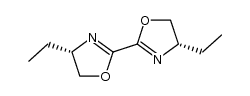
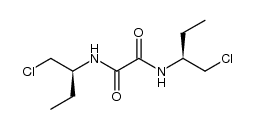



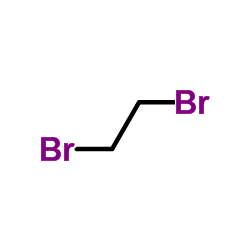
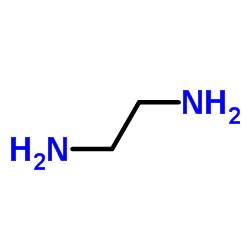 CAS#:107-15-3
CAS#:107-15-3