5-Methyl-N-(2-morpholino-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)furan-2-carboxamide
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 18:58:39
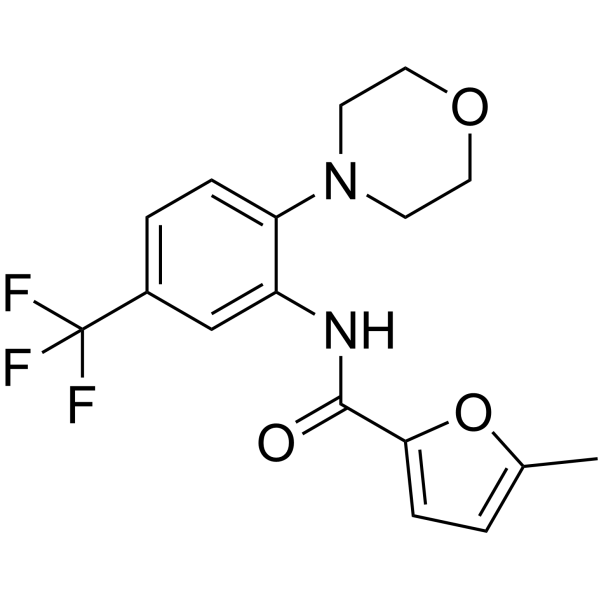
5-Methyl-N-(2-morpholino-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)furan-2-carboxamide structure
|
Common Name | 5-Methyl-N-(2-morpholino-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)furan-2-carboxamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 848057-98-7 | Molecular Weight | 354.324 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 391.2±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H17F3N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 190.4±27.9 °C | |
Use of 5-Methyl-N-(2-morpholino-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)furan-2-carboxamideSPHINX is a selective SRPK1 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 0.58 μM. SPHINX effectively reduces Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) in vivo. SPHINX can be used for the research of (age-related macular degenaration) AMD[1]. |
| Name | sphinx |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | SPHINX is a selective SRPK1 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 0.58 μM. SPHINX effectively reduces Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) in vivo. SPHINX can be used for the research of (age-related macular degenaration) AMD[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.58 μM (SRPK1)[1] |
| In Vitro | SPHINX (10 μM; 2 h) affects EGF-induced phosphorylation of SRSF1 and SRSF2[1]. SPHINX (5 μM; 24 h) reduces the expression of VEGF165 relative to GAPDH control either in primary RPE and ARPE-19 cell lines[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: ARPE-19 cell line Concentration: 10 μM Incubation Time: 2 hours Result: Blocked EGF-induced phosphorylation of SRSF1 and SRSF2. |
| In Vivo | SPHINX (10 ng; i.o. on laser photocoagulation day 0 and day 7) affects neovascular growth in vivo[1]. SPHINX (25 ng; i.o. on laser photocoagulation day 0 and day 7) affects the CNV area in CNV rats[1]. Animal Model: C57/B6 mice with laser-induced CNV[1] Dosage: 10 ng Administration: Intraocular injection; 10 ng on laser photocoagulation day 0 and day 7 Result: Significantly reduced neovascular growth compared with saline-injected controls. Animal Model: Norway Brown rats with laser-induced choroidal neovascularization[1] Dosage: 25 ng (10 ng/uL) Administration: Intraocular injection; 25 ng (10 ng/uL) on laser photocoagulation day 0 and day 7 Result: Significantly reduced the CNV area compared with saline injected controls. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 391.2±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H17F3N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 354.324 |
| Flash Point | 190.4±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 354.119141 |
| LogP | 4.01 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.555 |
| 2-Furancarboxamide, 5-methyl-N-[2-(4-morpholinyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]- |
| MFCD07315693 |
| 5-Methyl-N-[2-(4-morpholinyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-furamide |