AZT triphosphate
Modify Date: 2024-01-03 19:01:47
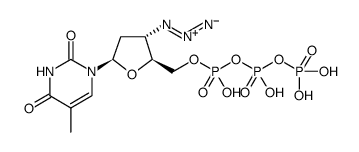
AZT triphosphate structure
|
Common Name | AZT triphosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 92586-35-1 | Molecular Weight | 507.18100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N5O13P3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of AZT triphosphateAZT triphosphate (3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-triphosphate) is a active triphosphate metabolite of Zidovudine (AZT). AZT triphosphate exhibits antiretroviral activity and inhibits replication of HIV. AZT triphosphate also inhibits the DNA polymerase of HBV. AZT triphosphate activates the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway[1][2][3]. |
| Name | Thymidine 5'-(tetrahydrogen triphosphate), 3'-azido-3'-deoxy |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | AZT triphosphate (3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-triphosphate) is a active triphosphate metabolite of Zidovudine (AZT). AZT triphosphate exhibits antiretroviral activity and inhibits replication of HIV. AZT triphosphate also inhibits the DNA polymerase of HBV. AZT triphosphate activates the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HIV[2] HBV[3] DNA polymerase[3] Reactive oxygen species (ROS)[1] |
| In Vitro | Treatment with 100 µM Zidovudine (AZT) for 48h disrupts the mitochondrial tubular network via accumulation of AZT triphosphate (AZT-TP) in H9c2 cells. AZT triphosphate accumulation causes downregulation of Opa1 and upregulation of Drp1. AZT triphosphate causes mitochondrial dysfunction, increases the production of cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS), and impairs the balance of the mitochondrial quality control system in H9c2 cell model established from rat embryonic myoblasts[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N5O13P3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 507.18100 |
| Exact Mass | 506.99600 |
| PSA | 303.09000 |
| 3'-Azidothymidine triphosphate |
| 3'-AZIDO-3'-DEOXYTHYMIDINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE |
| AZTTP |
| 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate |
| 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine triphosphate |
| AZT triphosphate |