Combined bioaugmentation with anaerobic ruminal fungi and fermentative bacteria to enhance biogas production from wheat straw and mushroom spent straw
Alberto Ferraro, Giulia Dottorini, Giulia Massini, Valentina Mazzurco Miritana, Antonella Signorini, Giuseppe Lembo, Massimiliano Fabbricino
文献索引:10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.128
全文:HTML全文
摘要
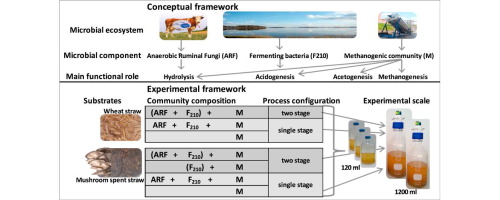
Bioaugmentation with anaerobic ruminal fungi and a pool of hydrogen-producing fermenting bacteria was tested on wheat straw (WS) and mushroom spent straw (MSS) with the aim of improving anaerobic digestion performance. Batch tests were set up to simulate a Bioaugmentation Anaerobic Digestion (BAD) treatment comparing single- (I-BAD) and two-stage (II-BAD) process configurations, at two reactor scales, 120 and 1200 ml (×10). In both cases, higher CH4 cumulative production was obtained in the II-BAD configuration on WS (65.1±8.9 Nml and 922±73.8 Nml respectively). The II-BADx10 tests allowed increasing CH4 production (≃290% and ≃330% on WS and MSS, respectively) when compared to the unaugmented condition. Final results highlighted the achievable advantages of the two stage configuration in terms of CH4 production enhancement. Microbial community investigations confirmed the efficiency of the bioaugmentation treatment and revealed that such a result was mainly related to the Methanosarcinales increase, mostly composed by Methanosaeta.
|
Sustainable green pretreatment approach to biomass-to-energy...
2018-04-12 [10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.039] |
|
Adsorption removal of natural organic matters in waters usin...
2018-04-07 [10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.016] |
|
Biodegradation of acrylamide by a novel isolate, Cupriavidus...
2018-04-06 [10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.012] |
|
Biocatalytic strategies for the production of high fructose ...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.127] |
|
High-frequency, high-intensity electromagnetic field effects...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.130] |