| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
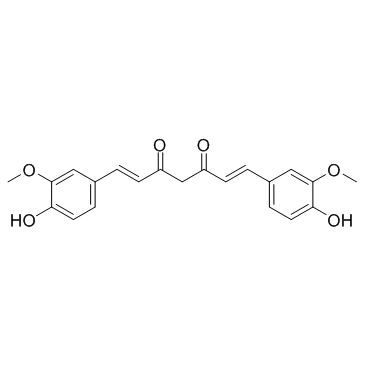 |
姜黄素
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
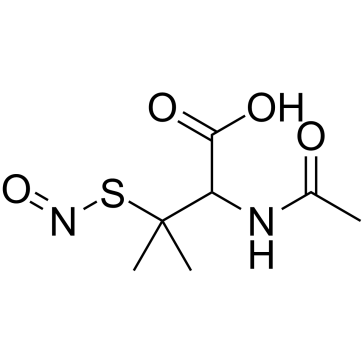 |
S-亚硝基-N-乙酰-DL-青霉胺
CAS:67776-06-1 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
姜黄素
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
 |
S-亚硝基-N-乙酰-DL-青霉胺
CAS:67776-06-1 |